Qatar Hydrogeological Assessment Project (QHAP)
PURPOSES
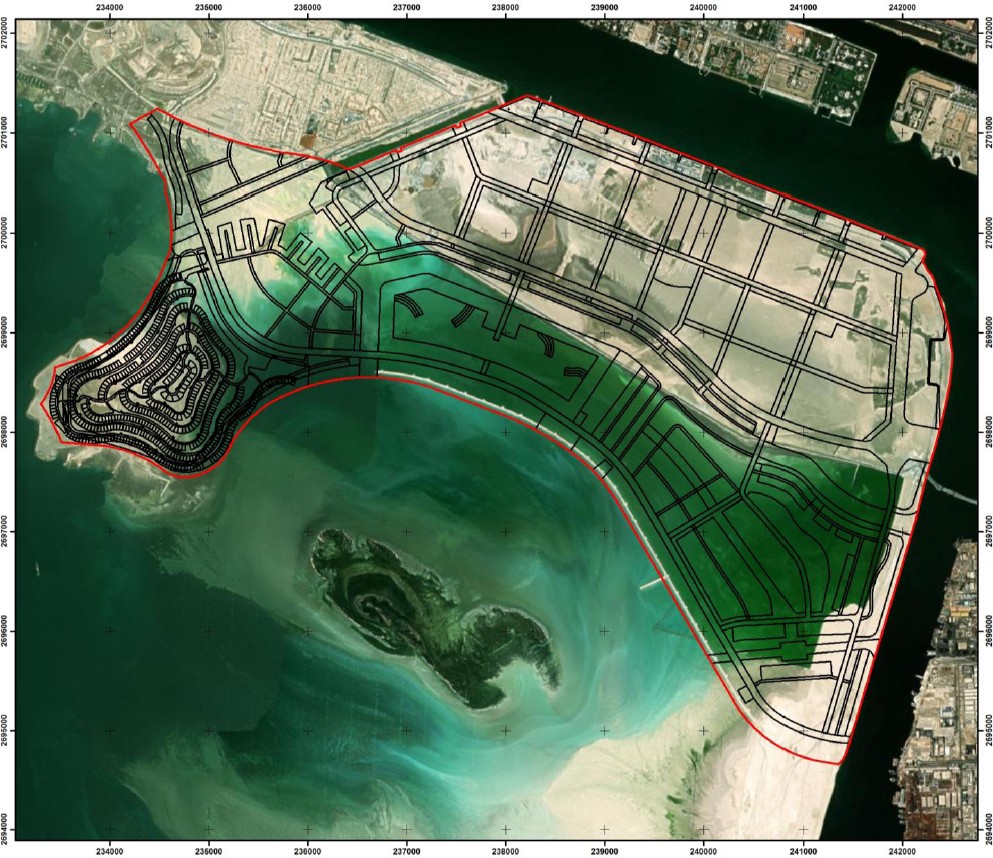
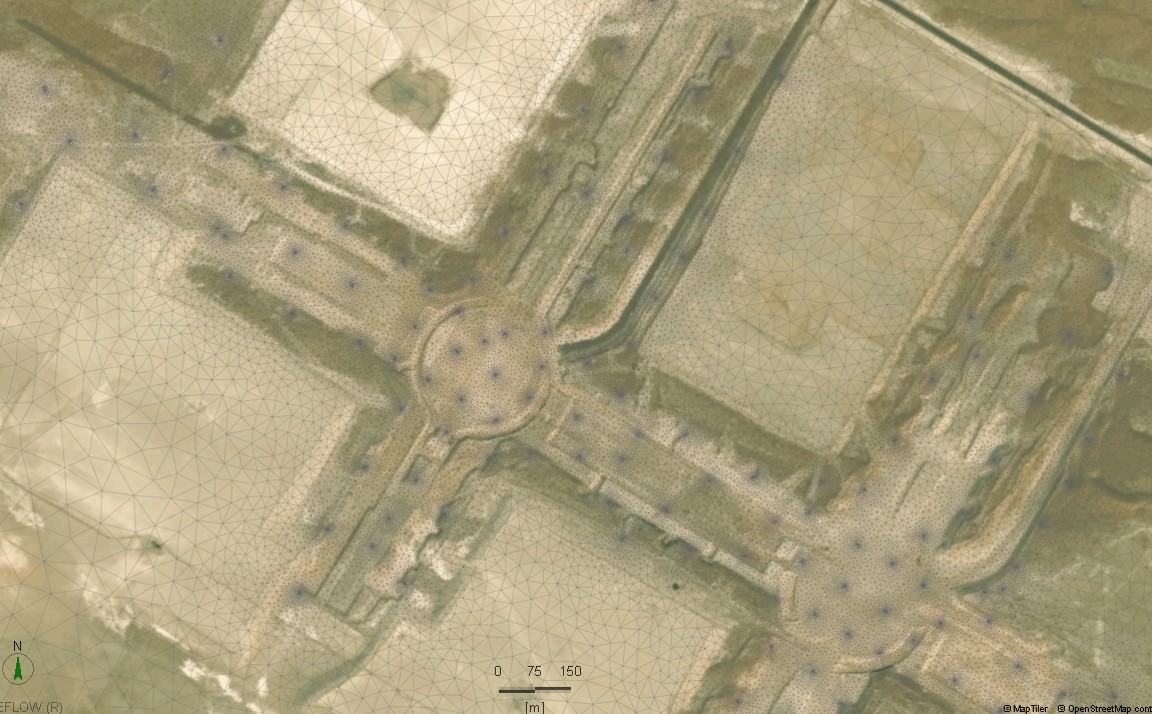
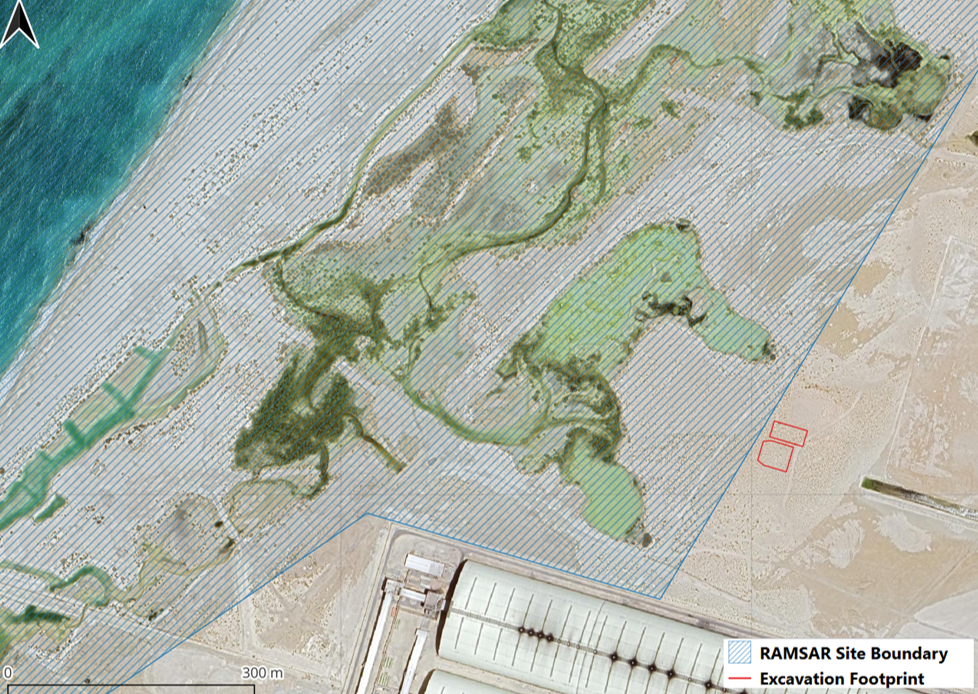
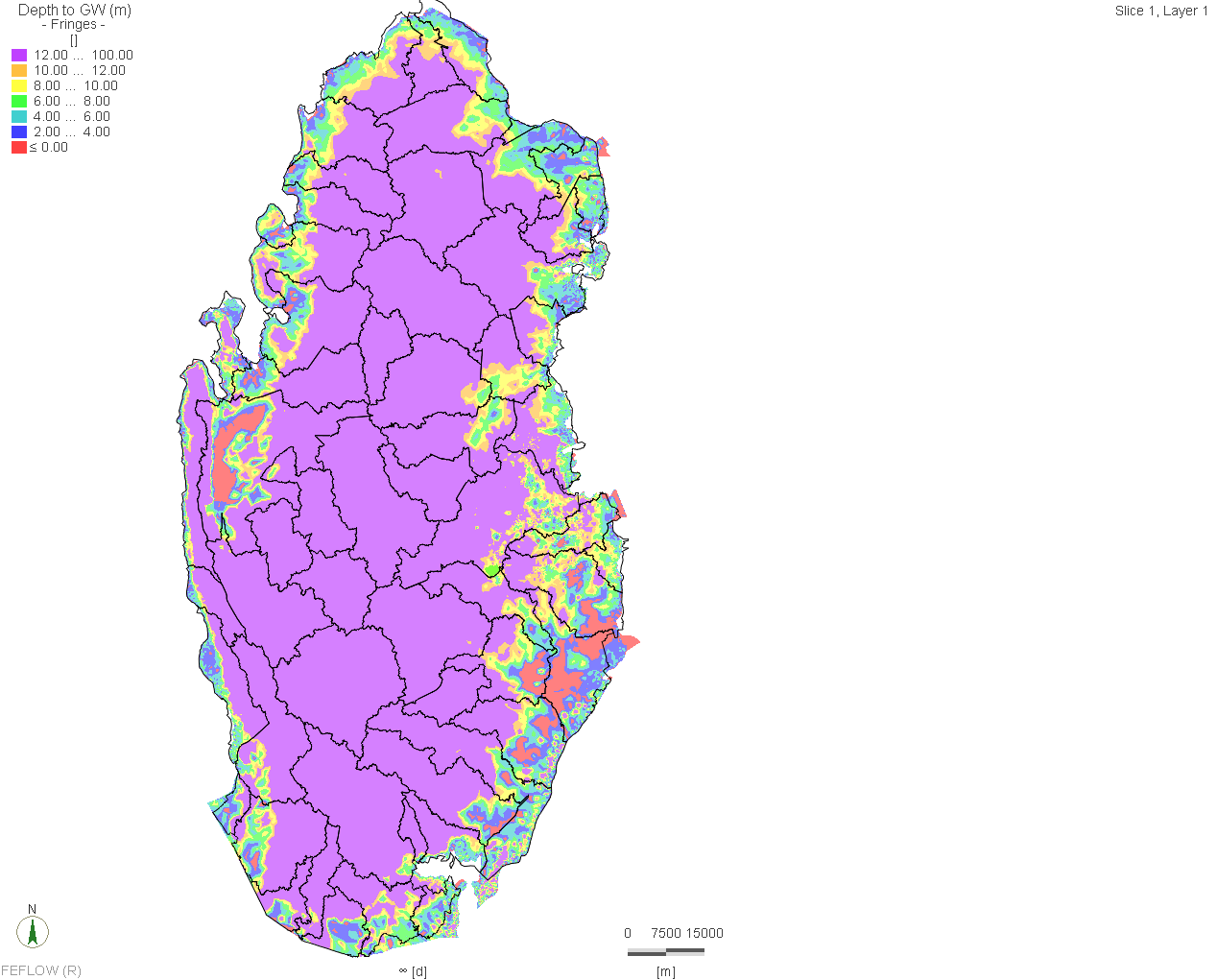
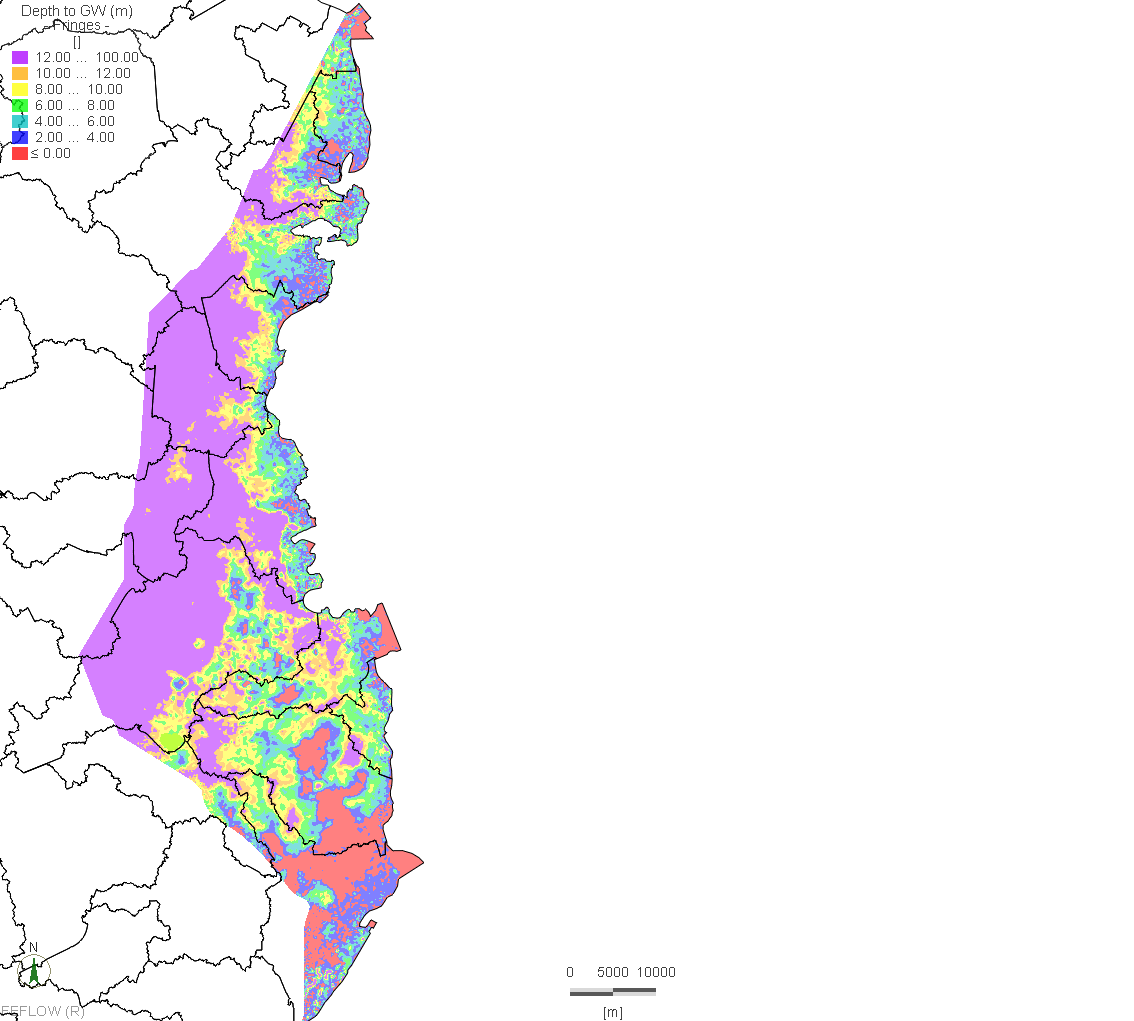
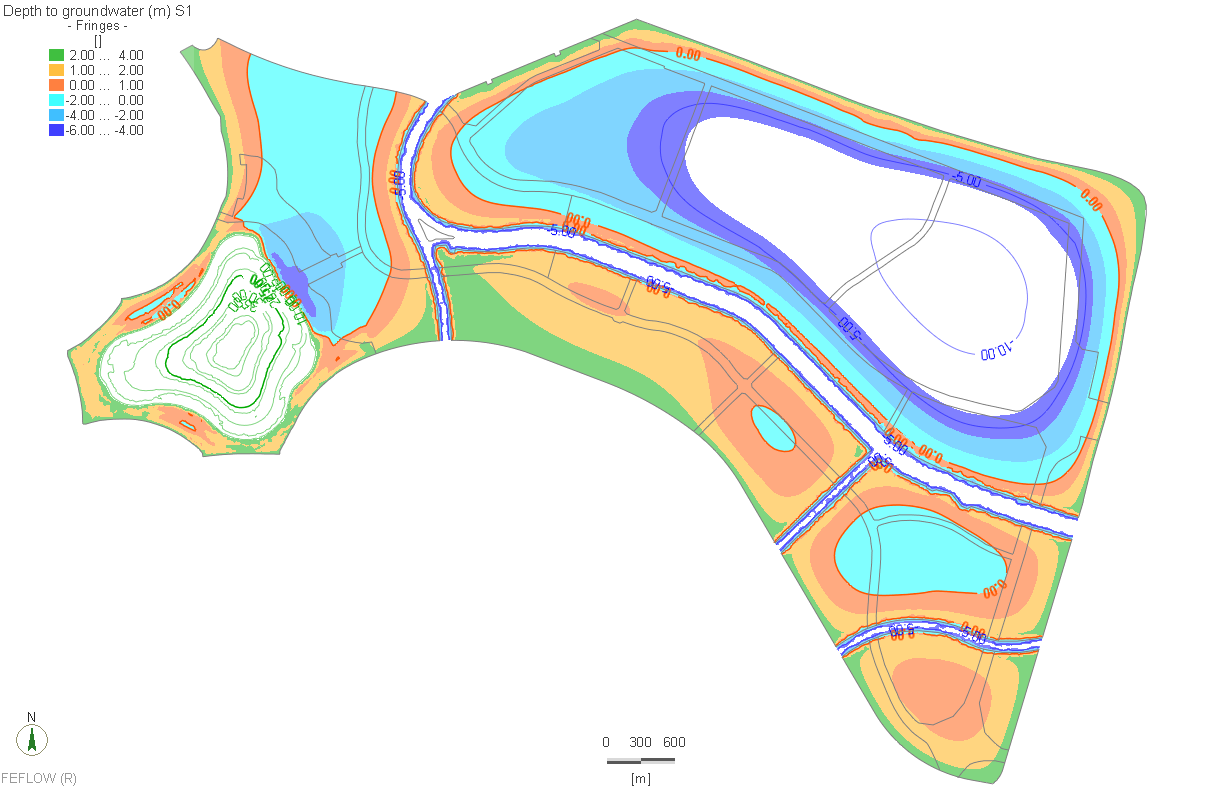
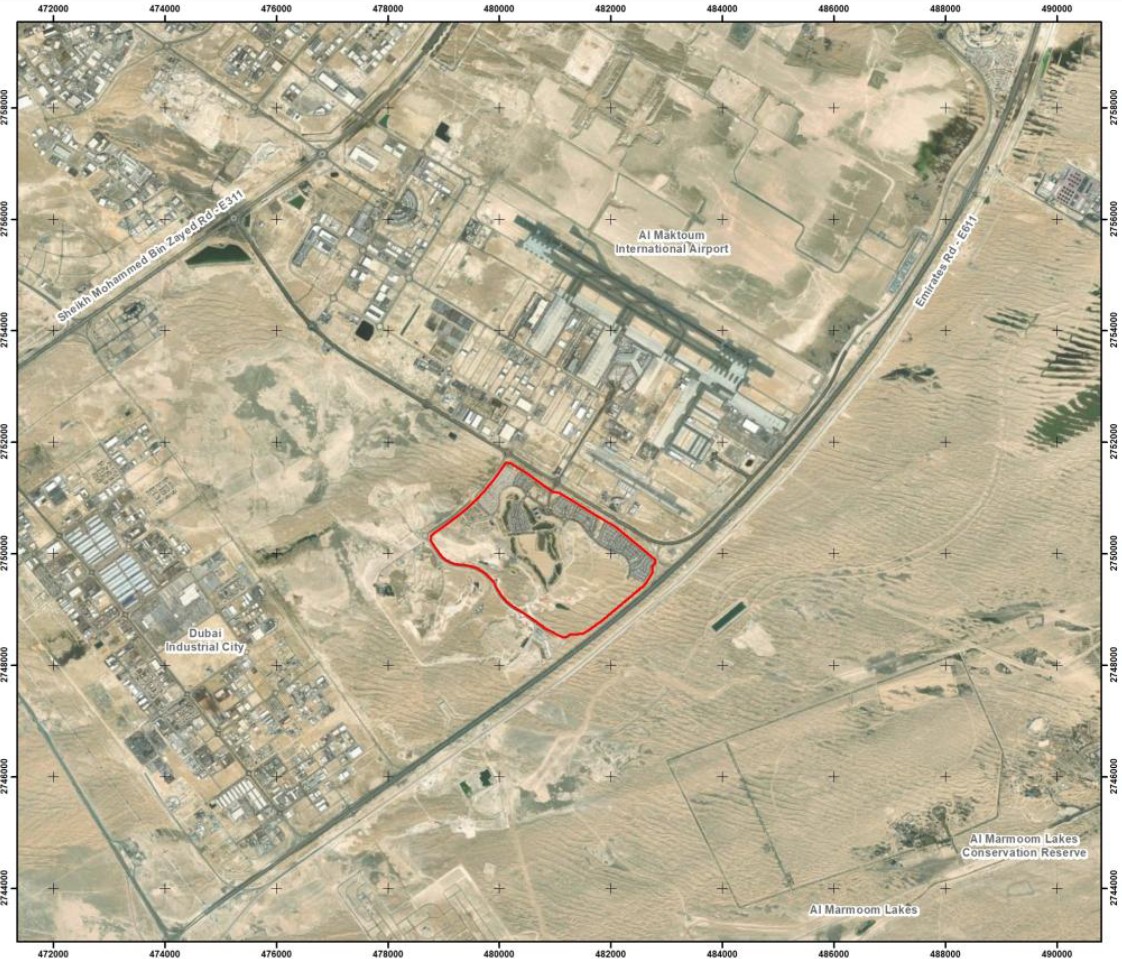
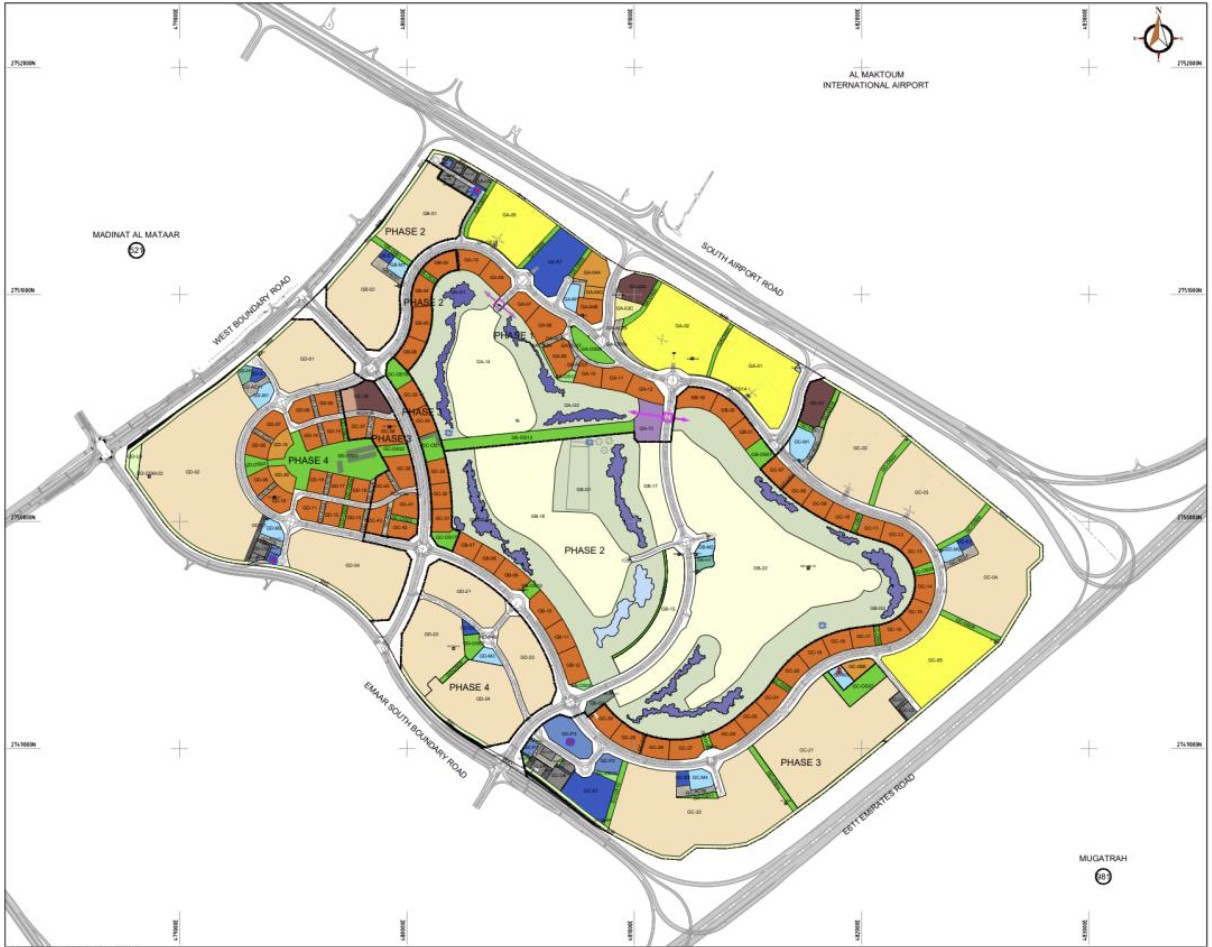
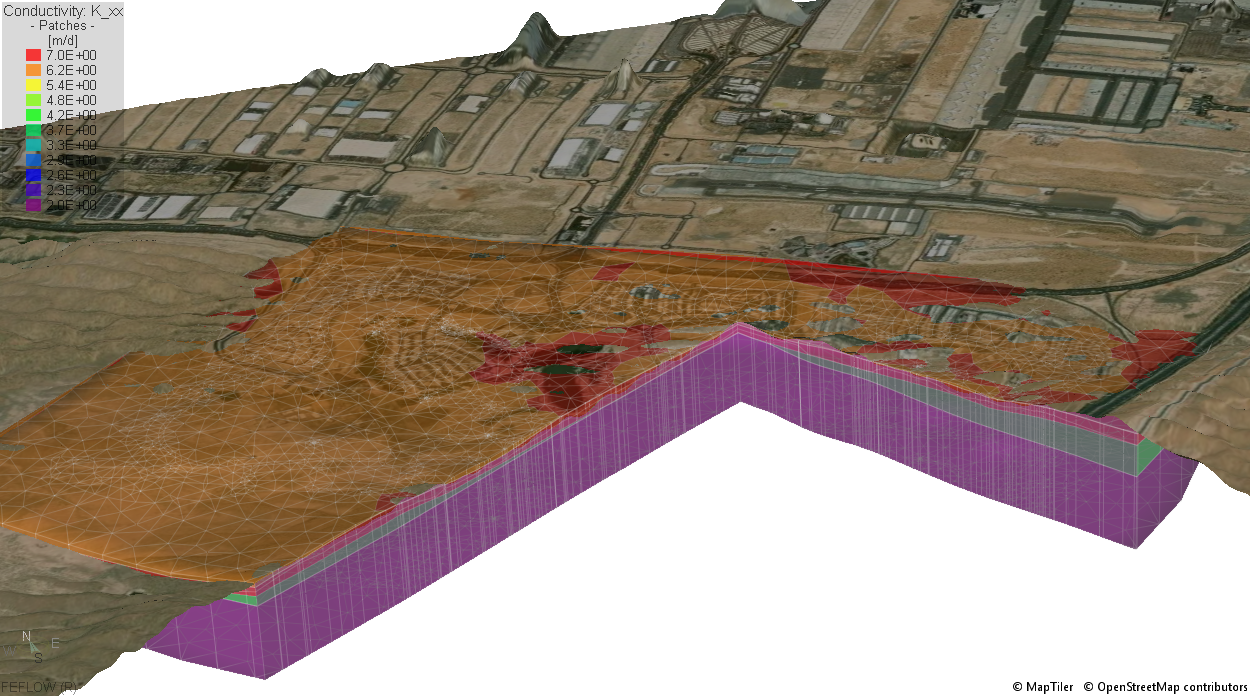
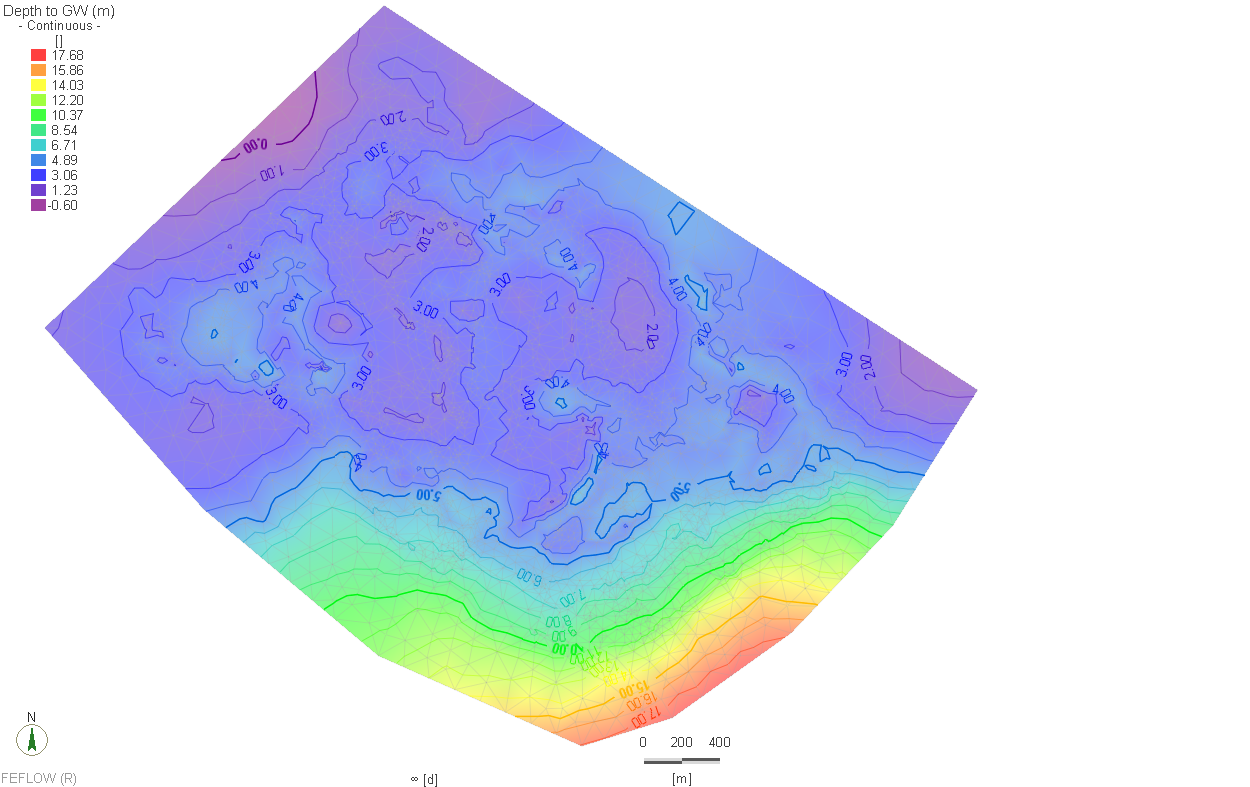
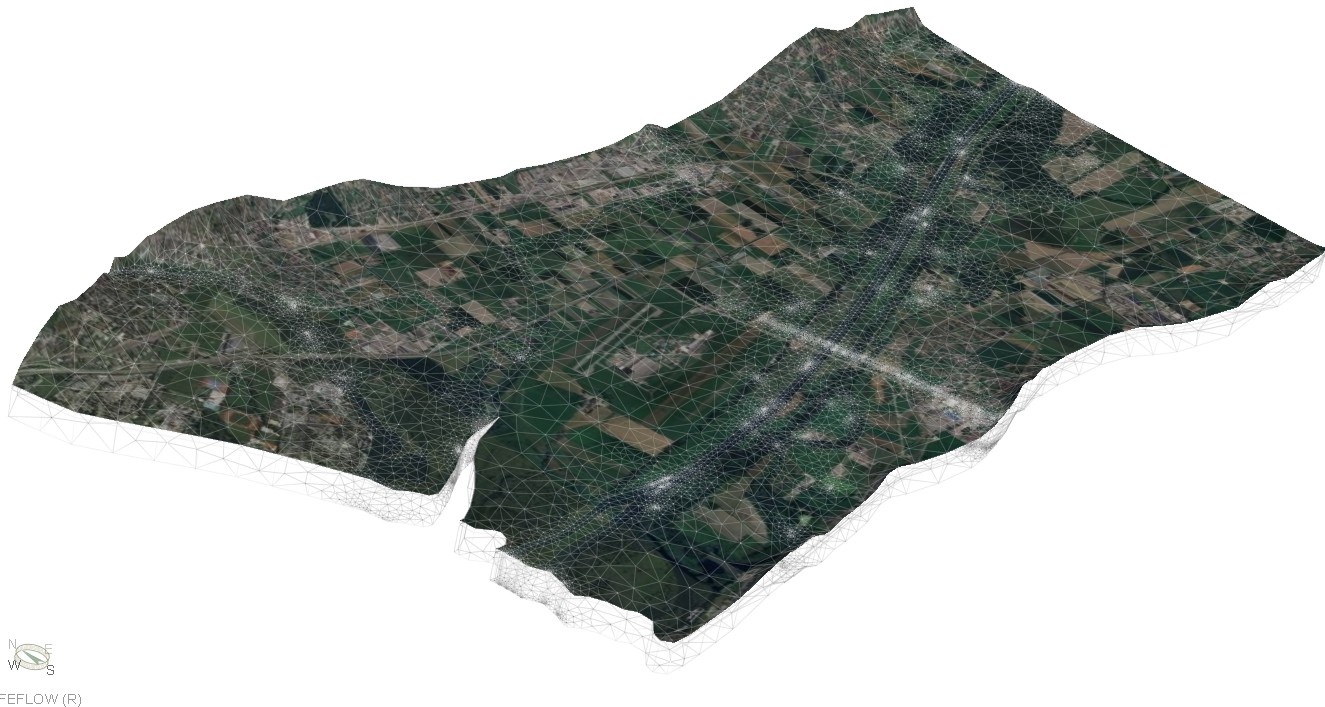
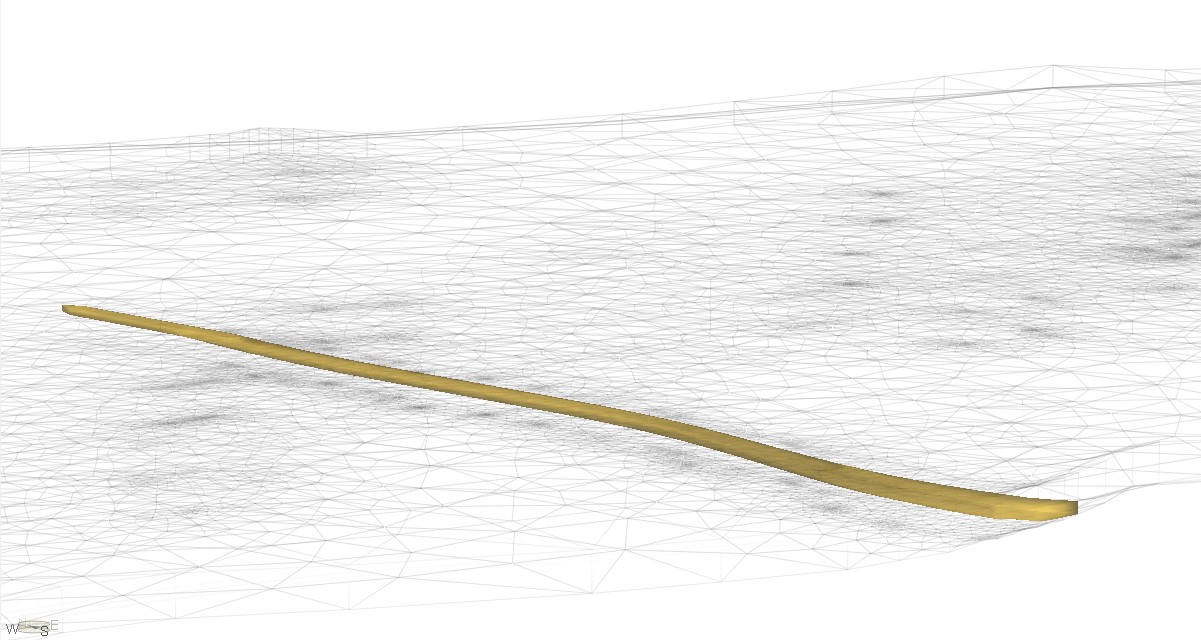
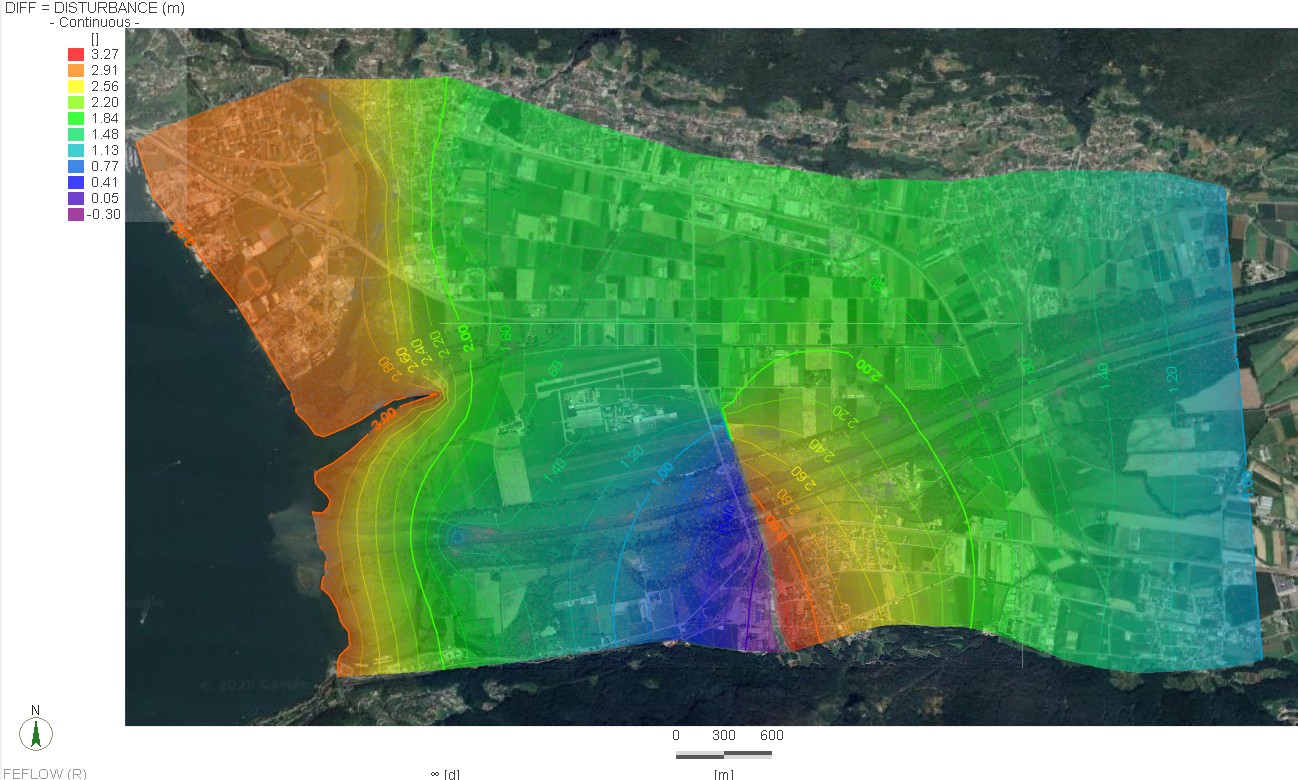
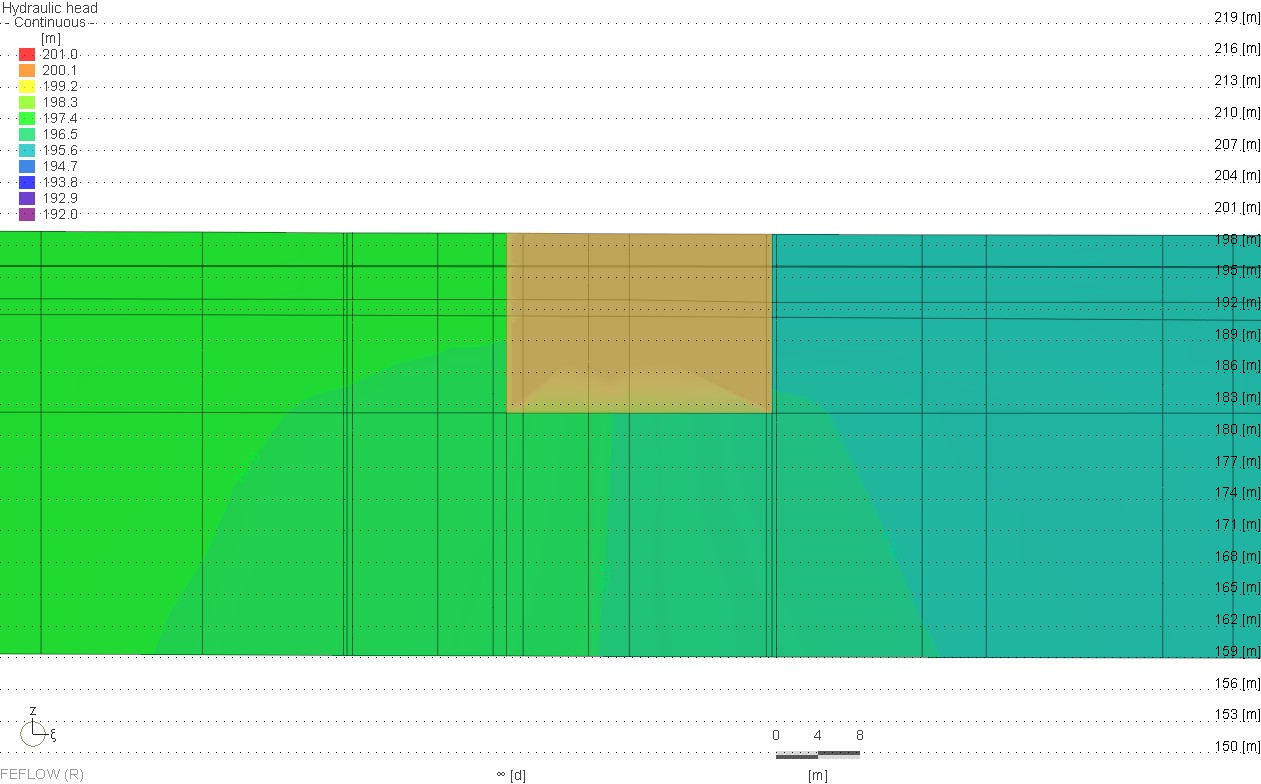
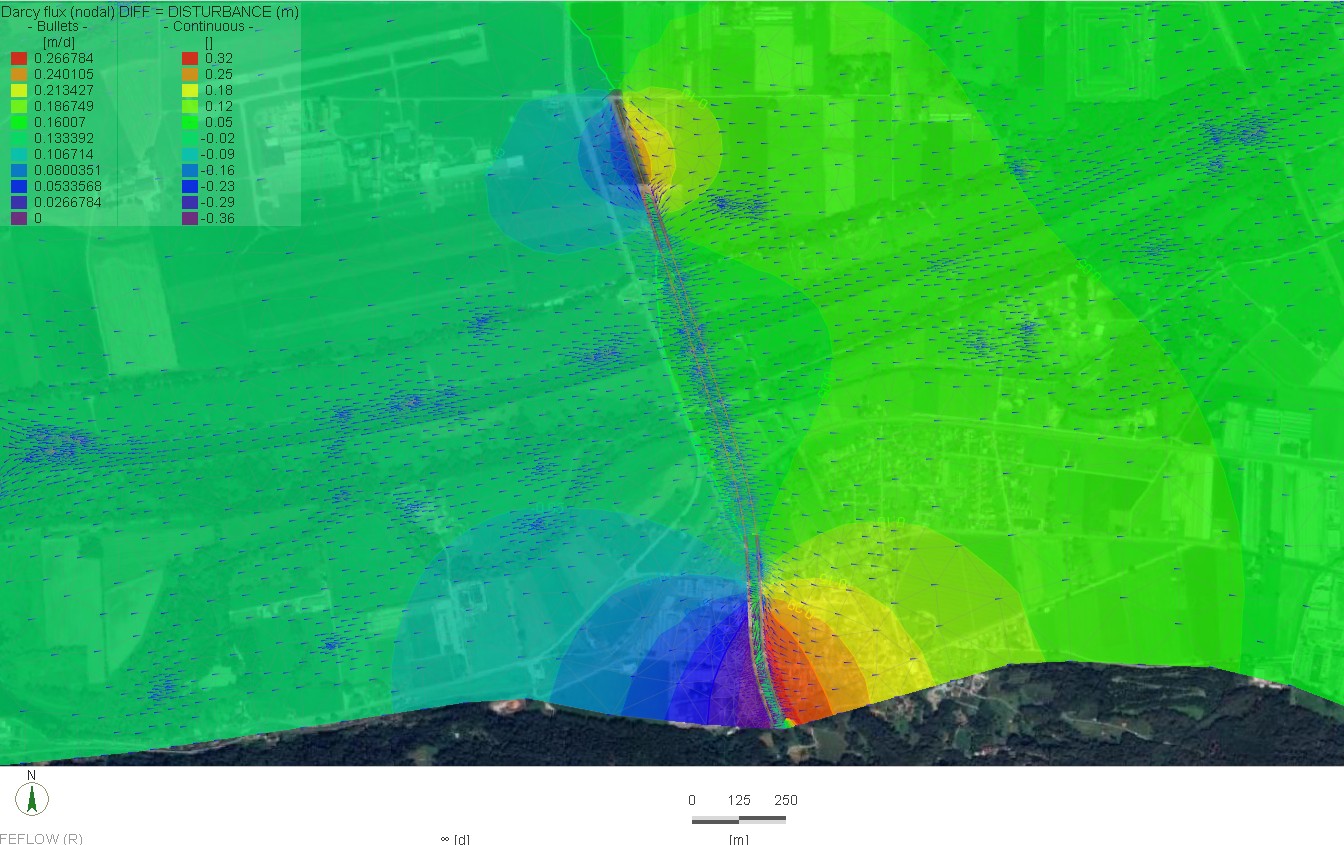
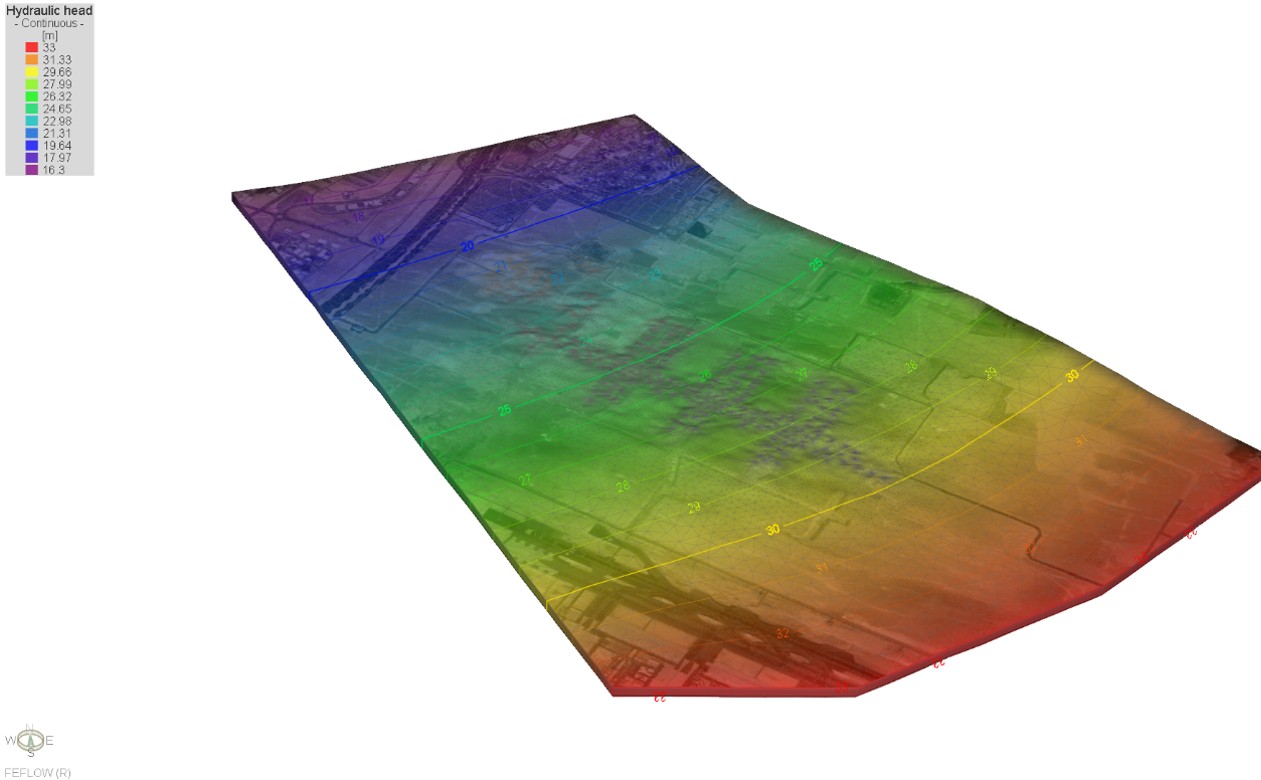
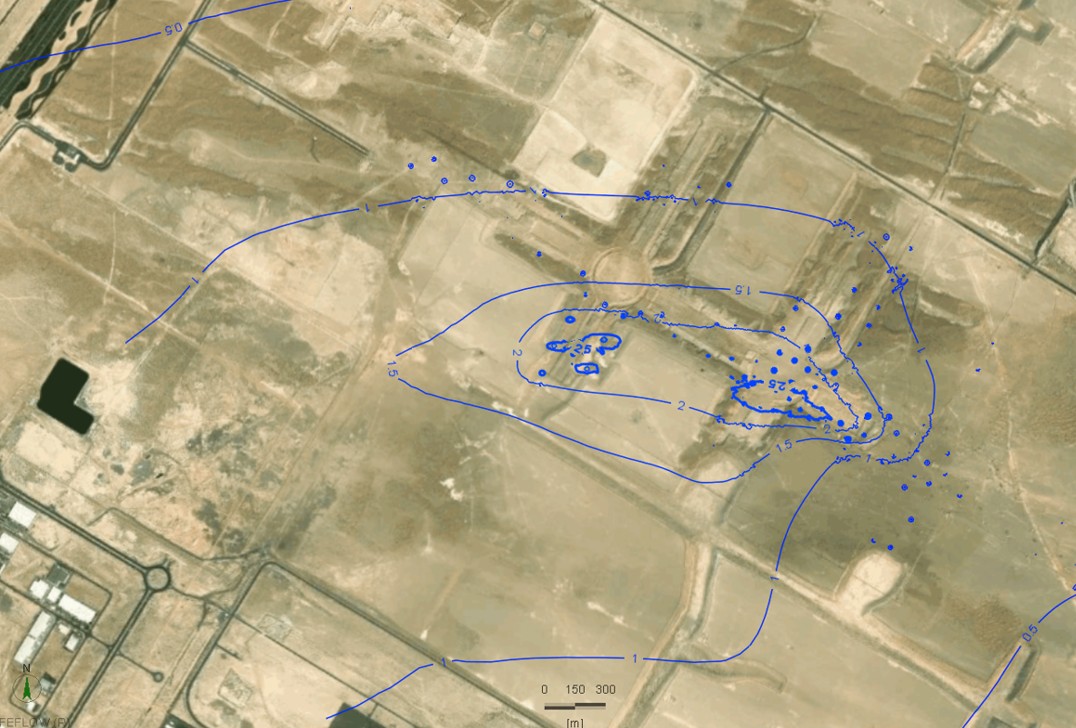
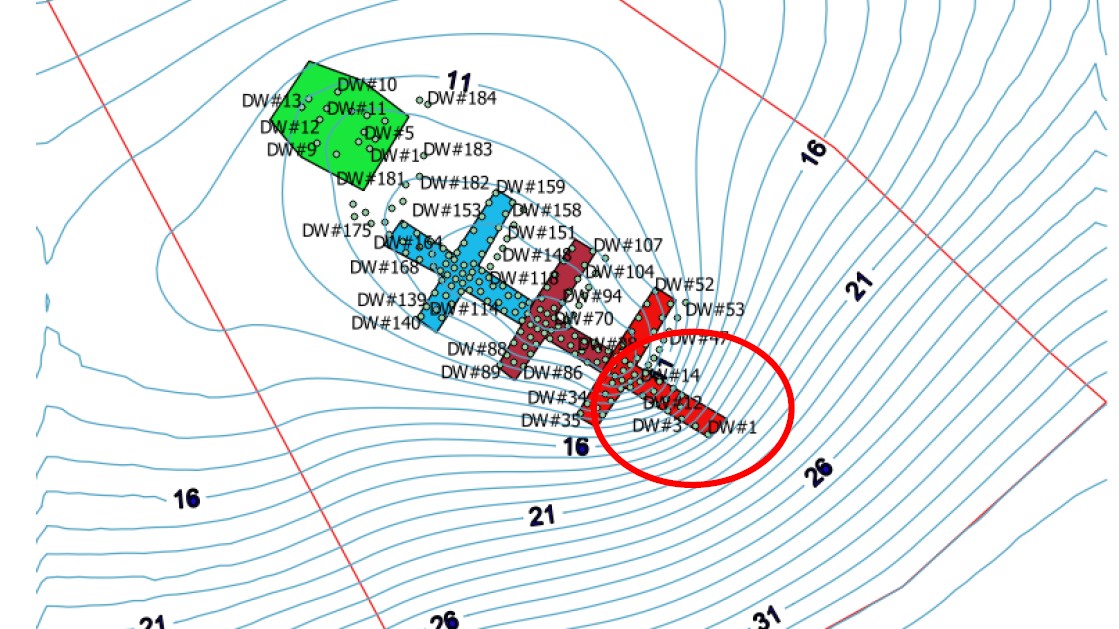
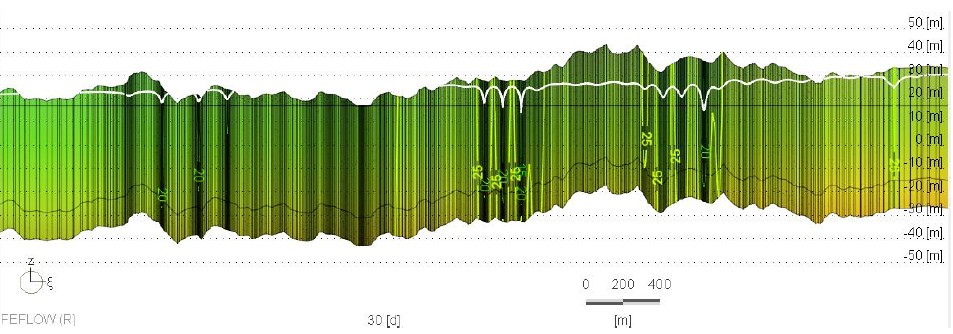
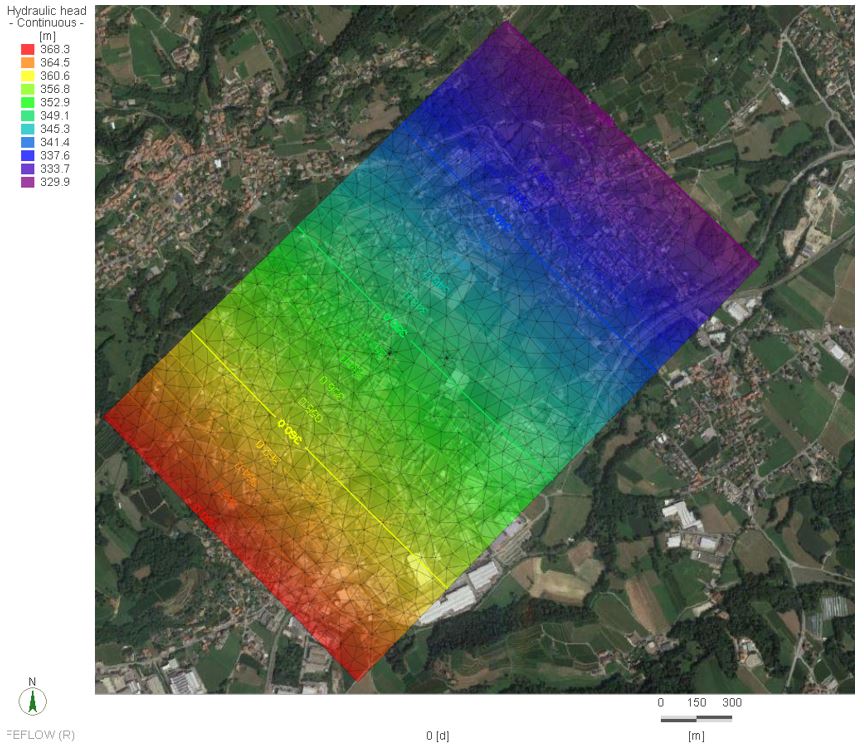
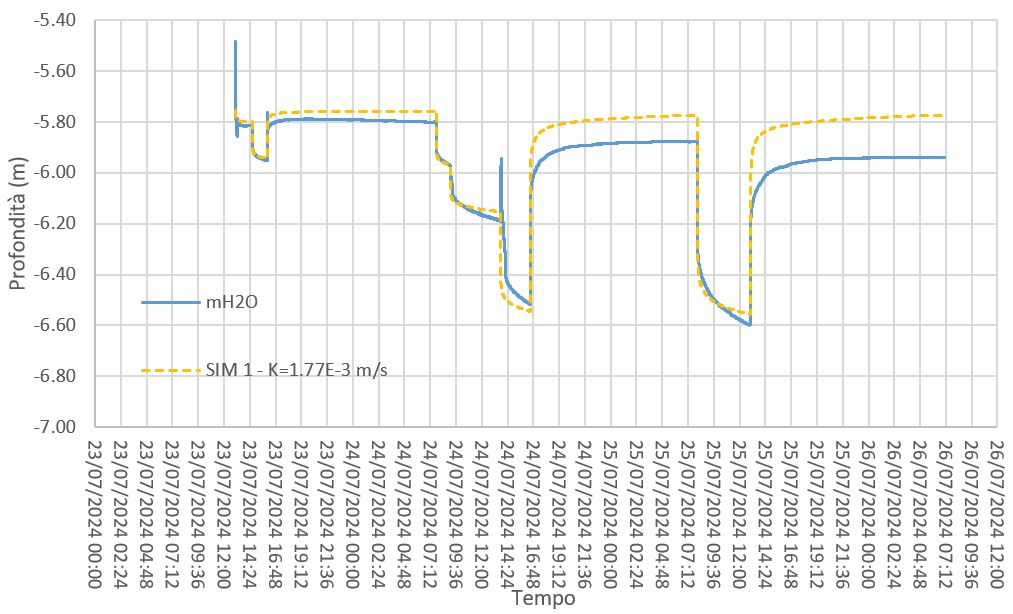
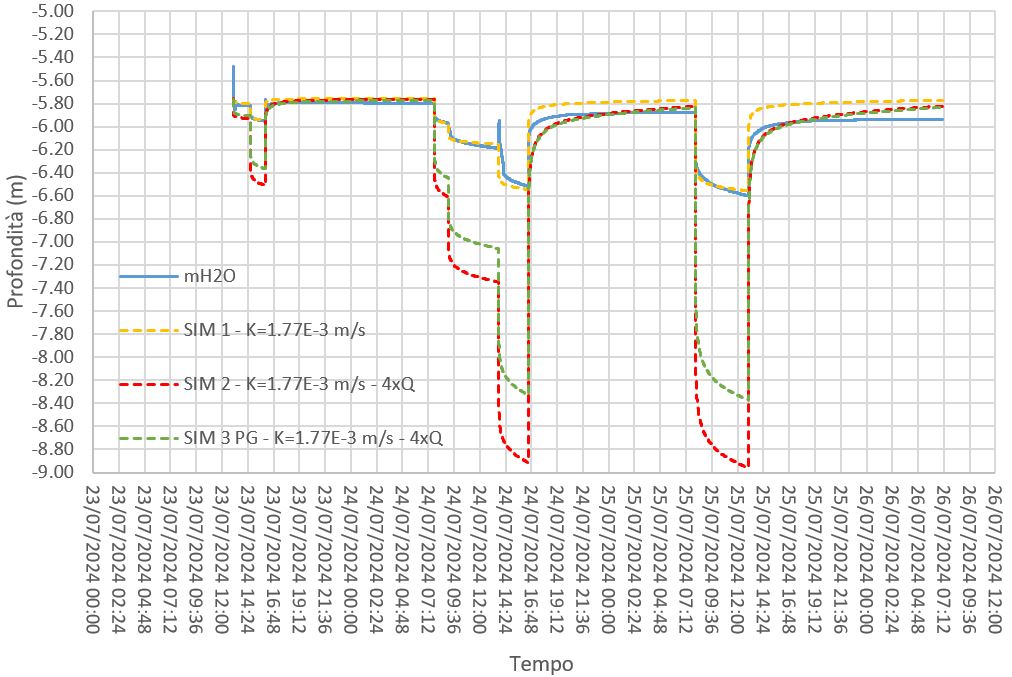
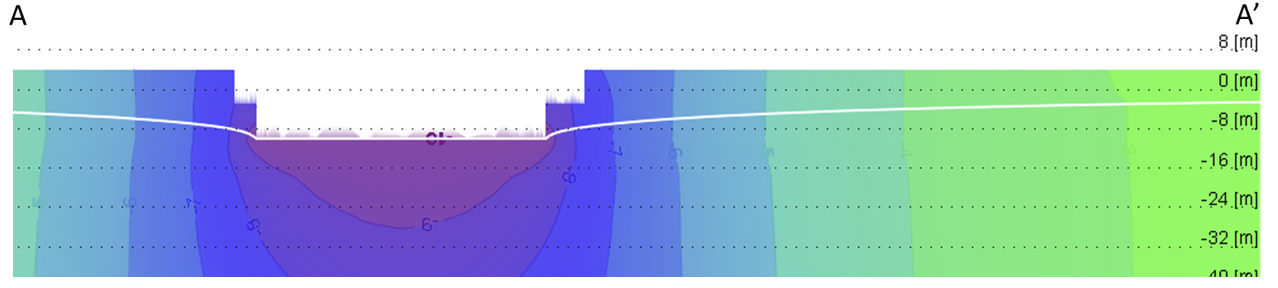
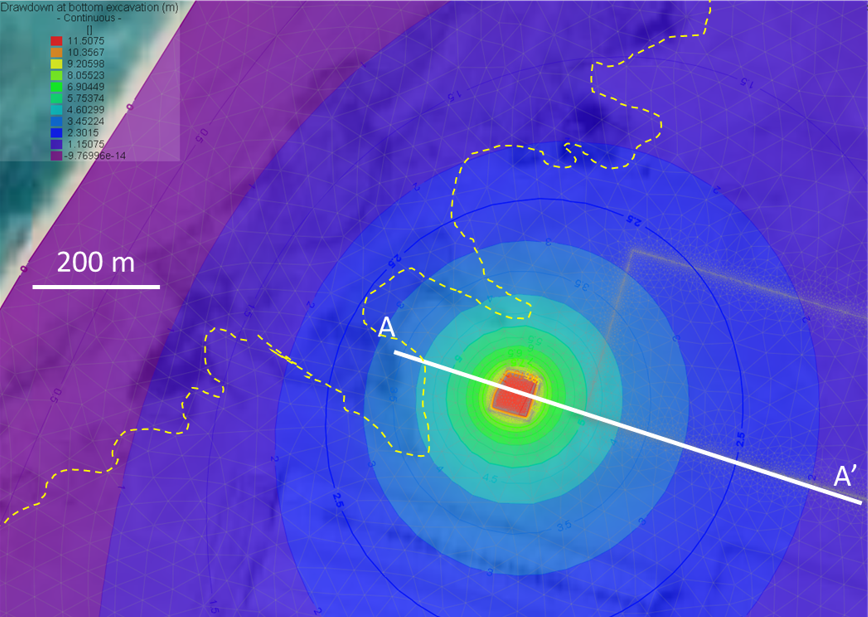
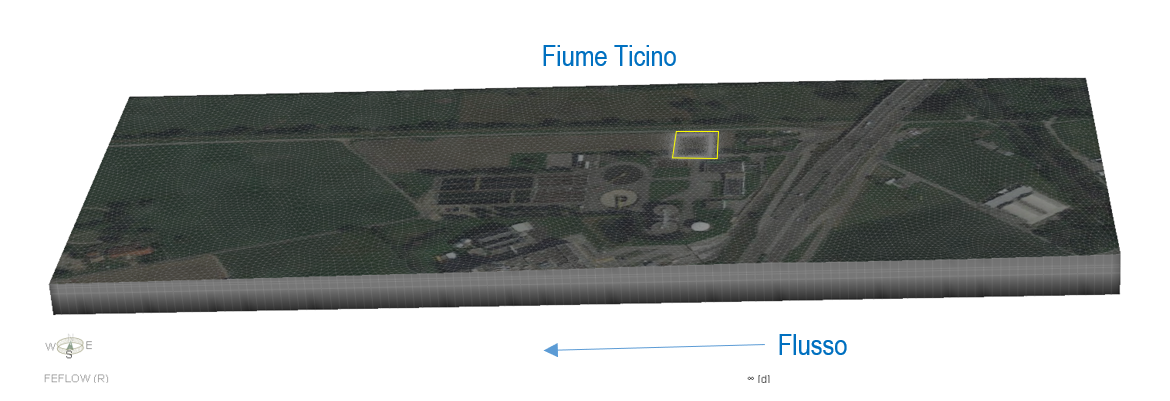
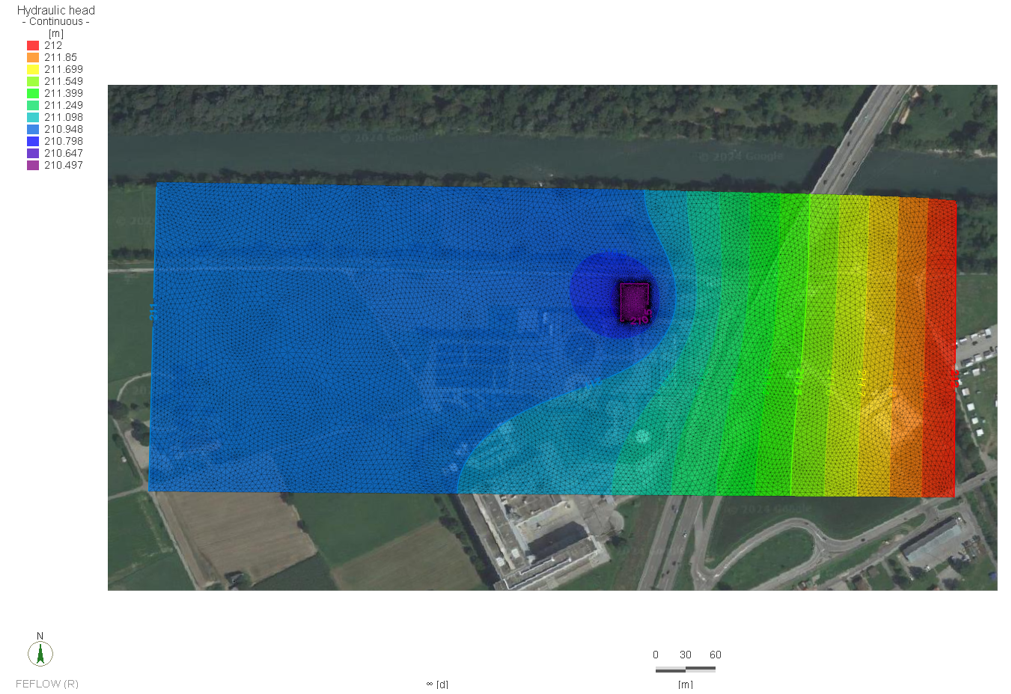
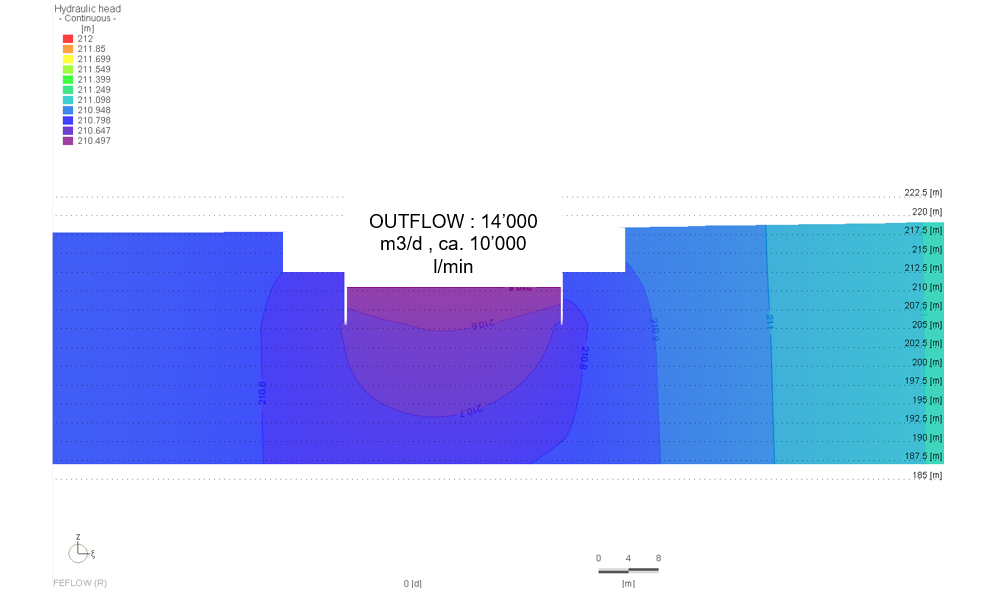
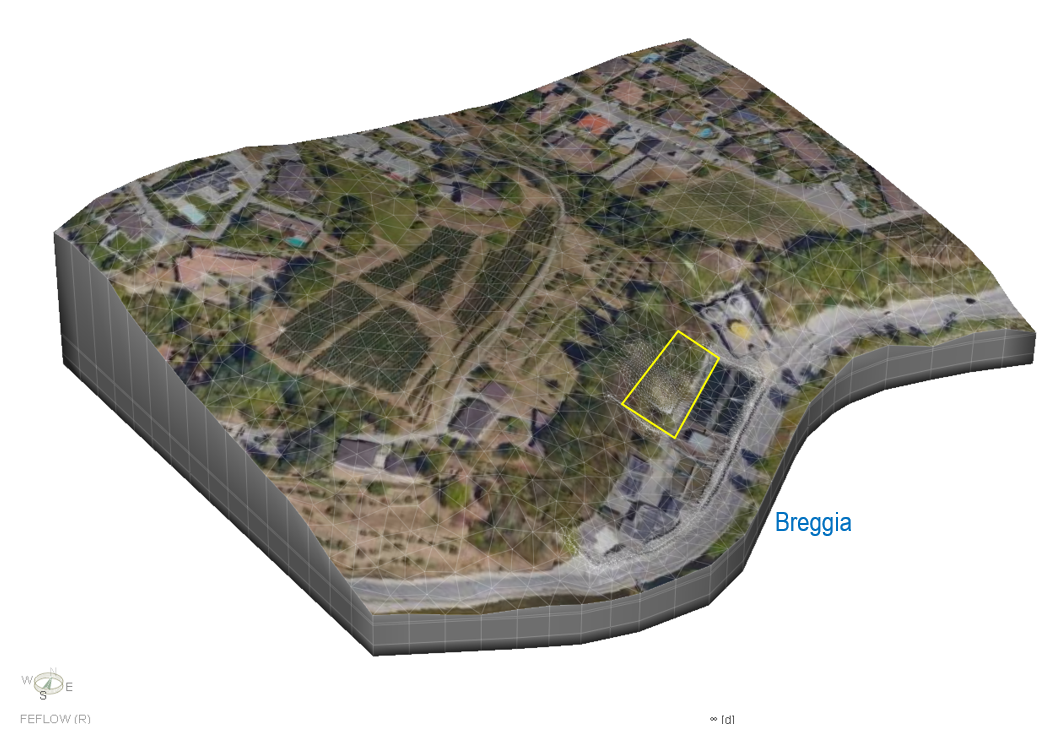
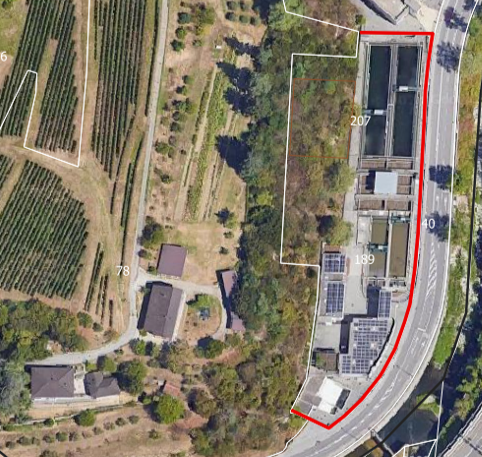
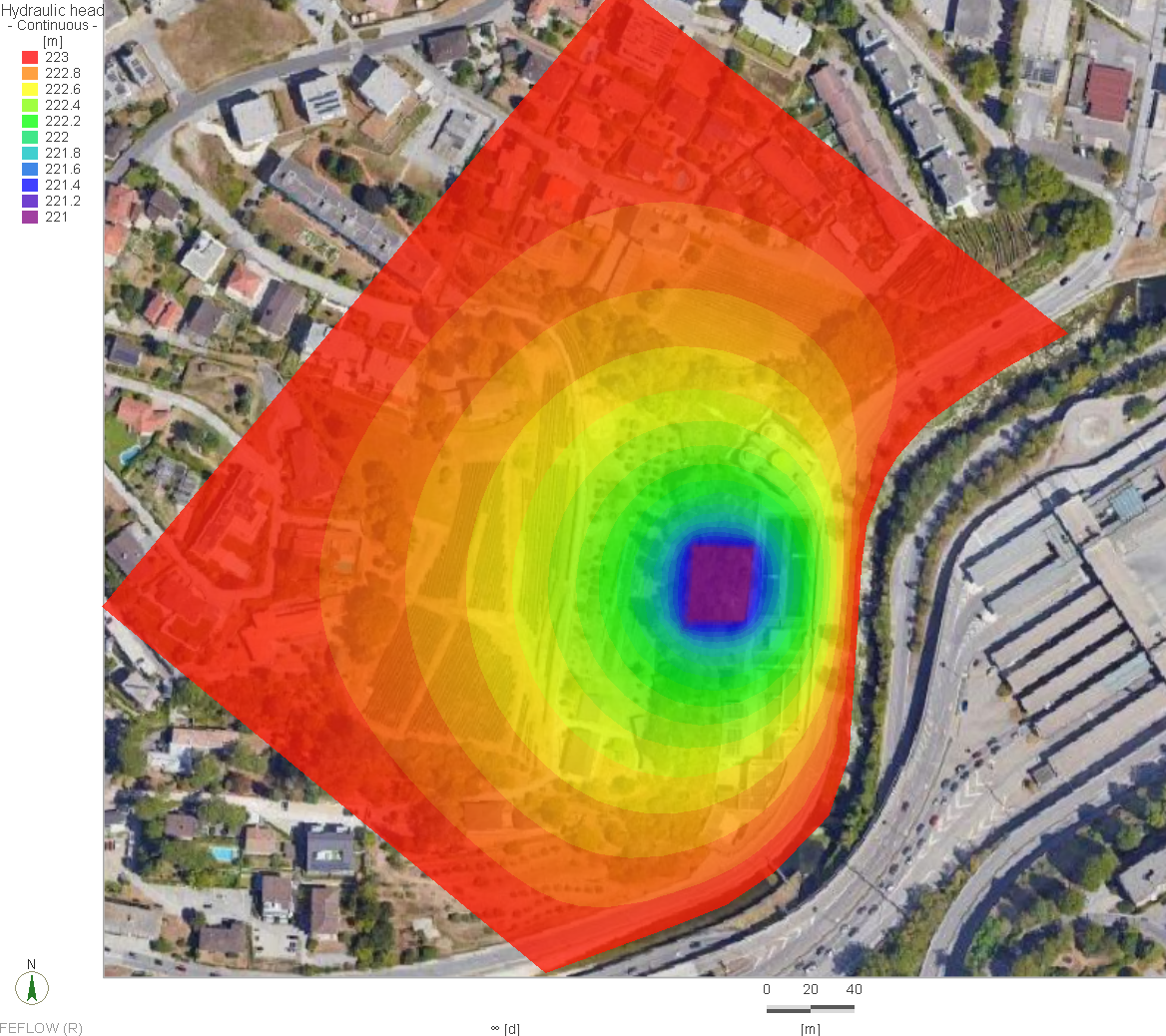
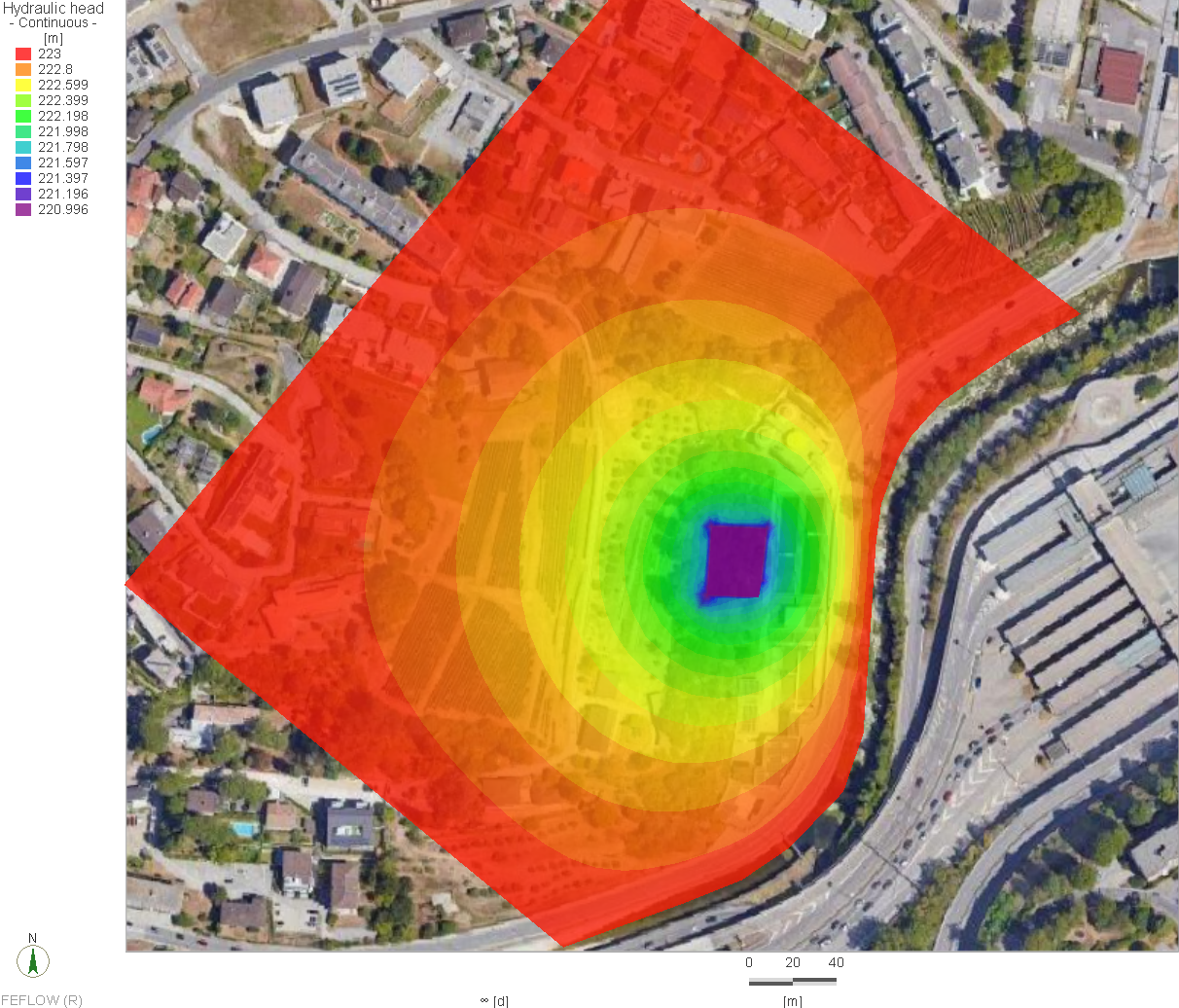
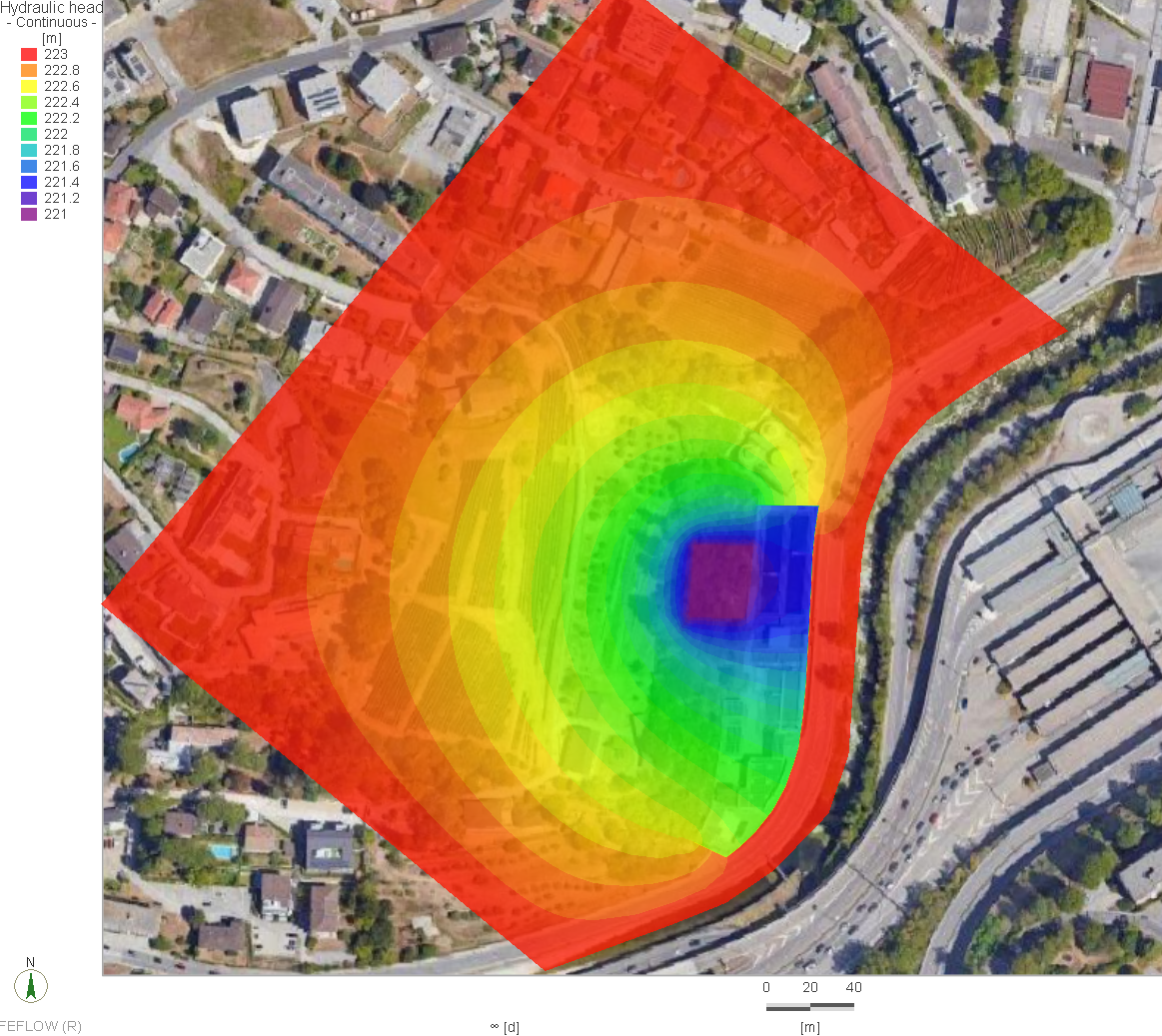
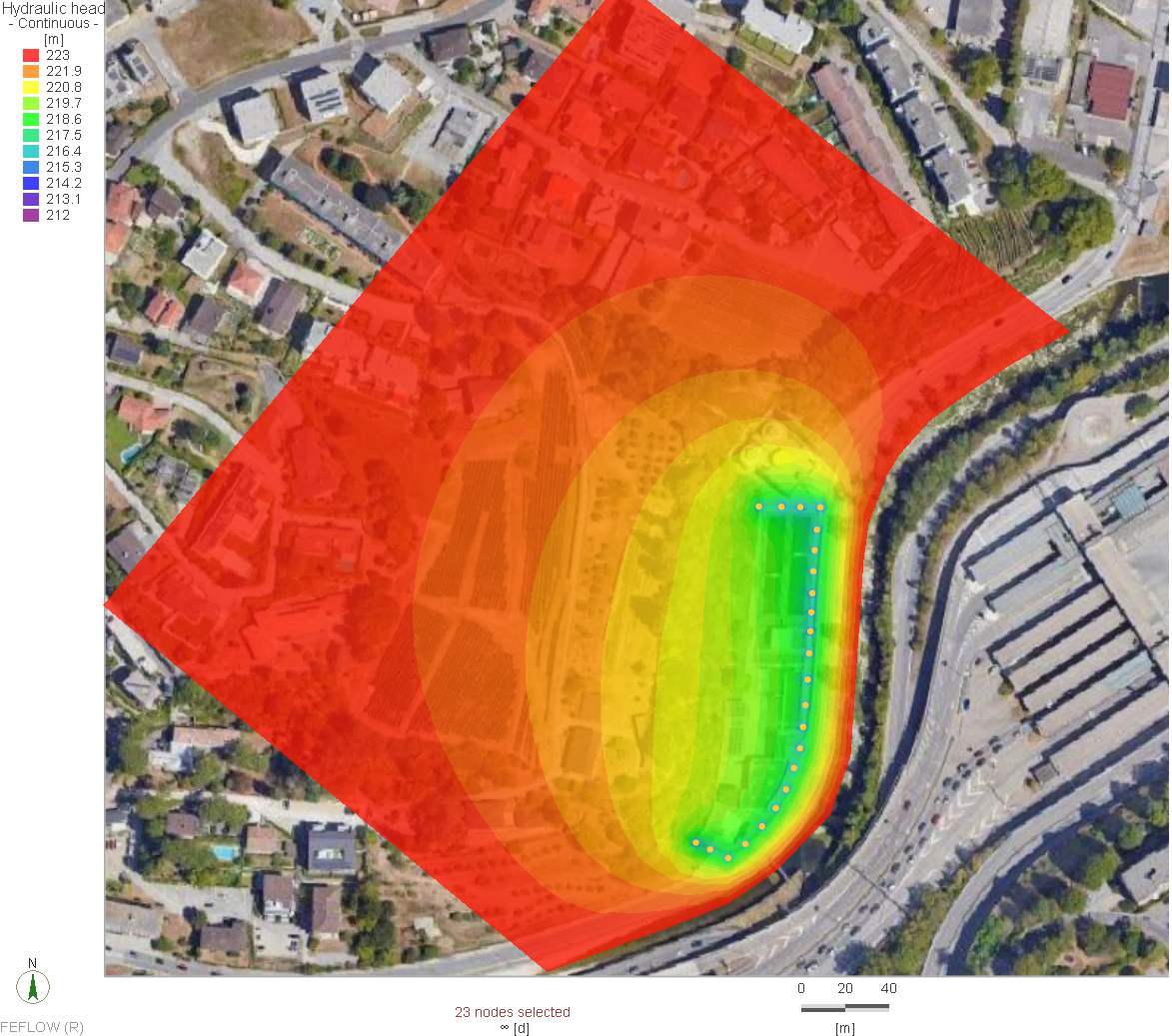
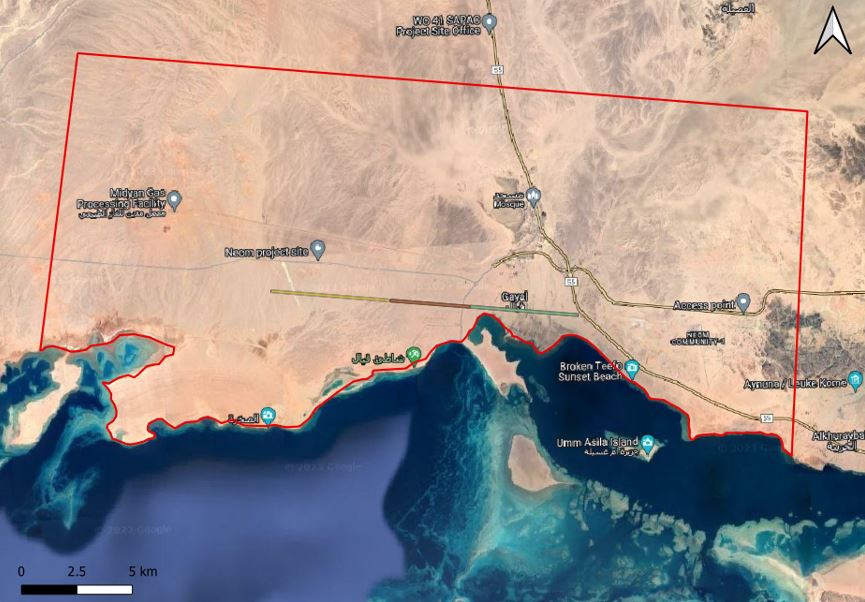
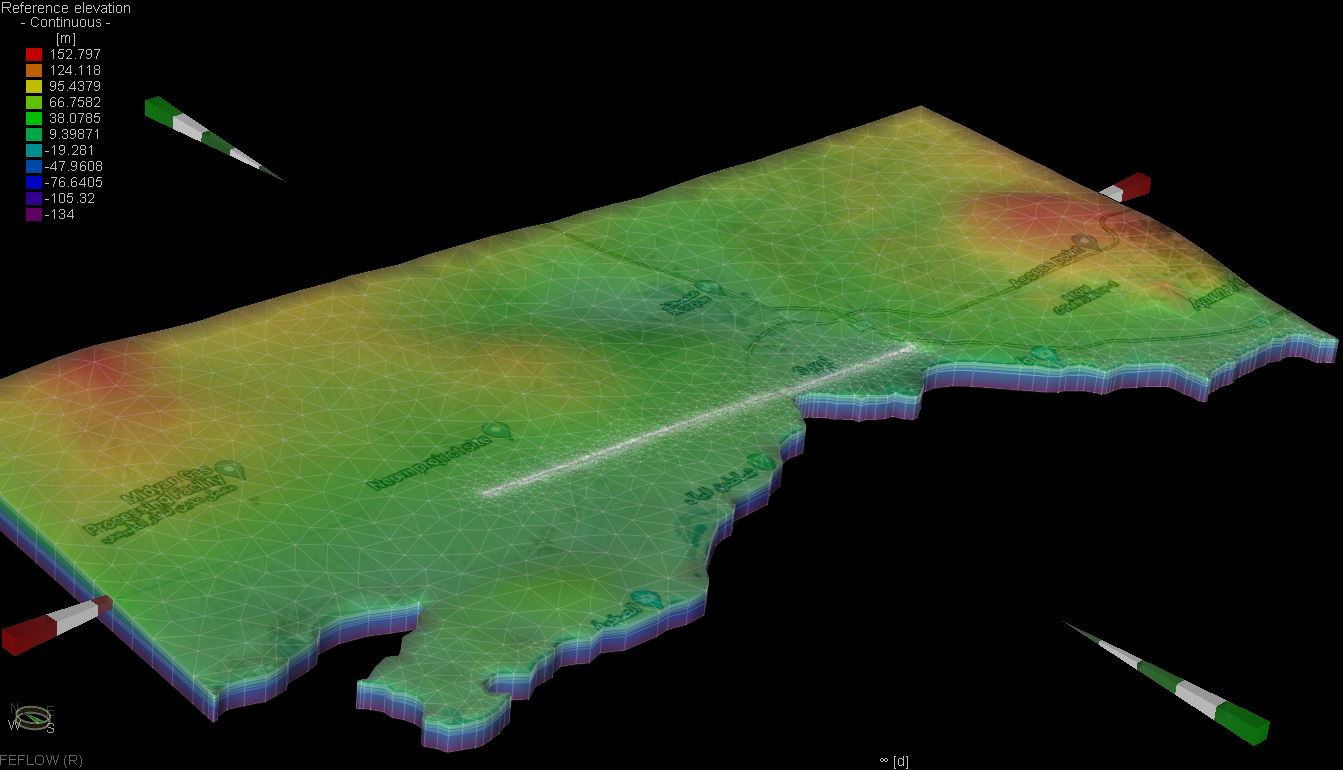
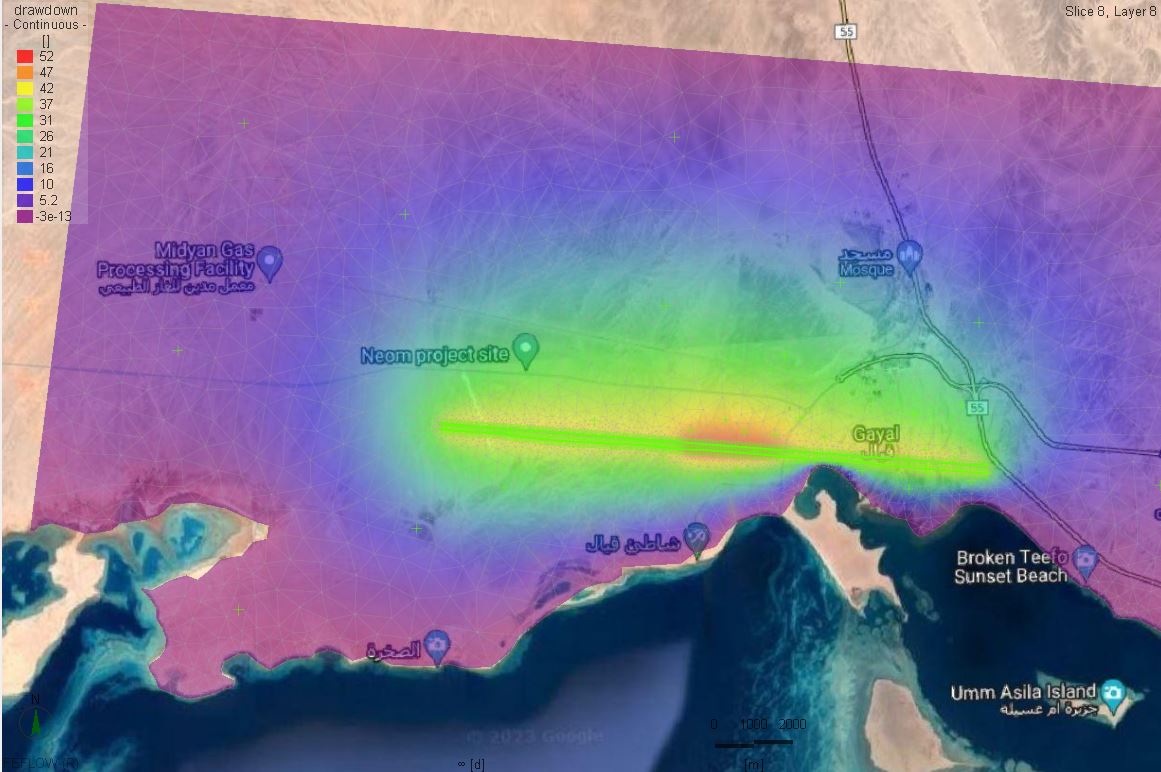
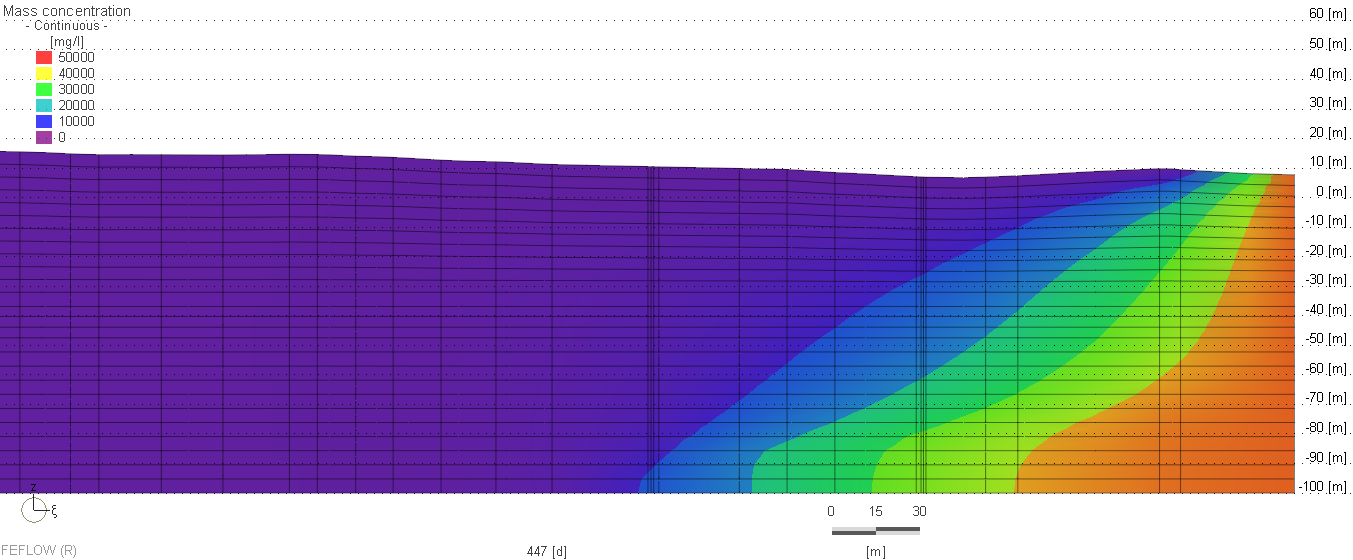
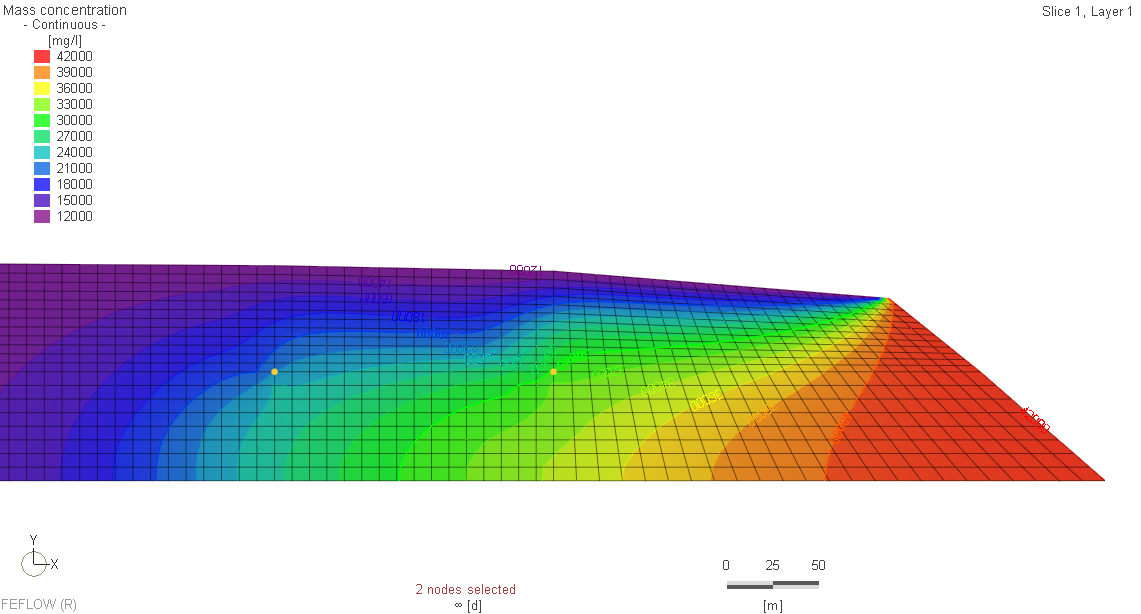
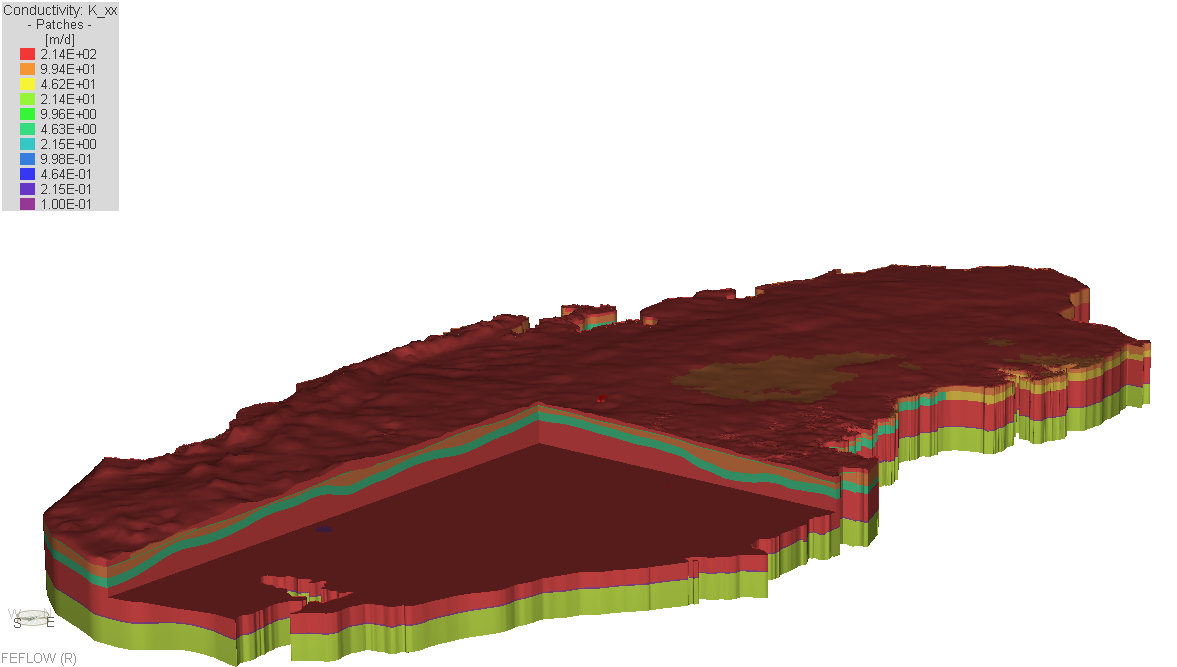
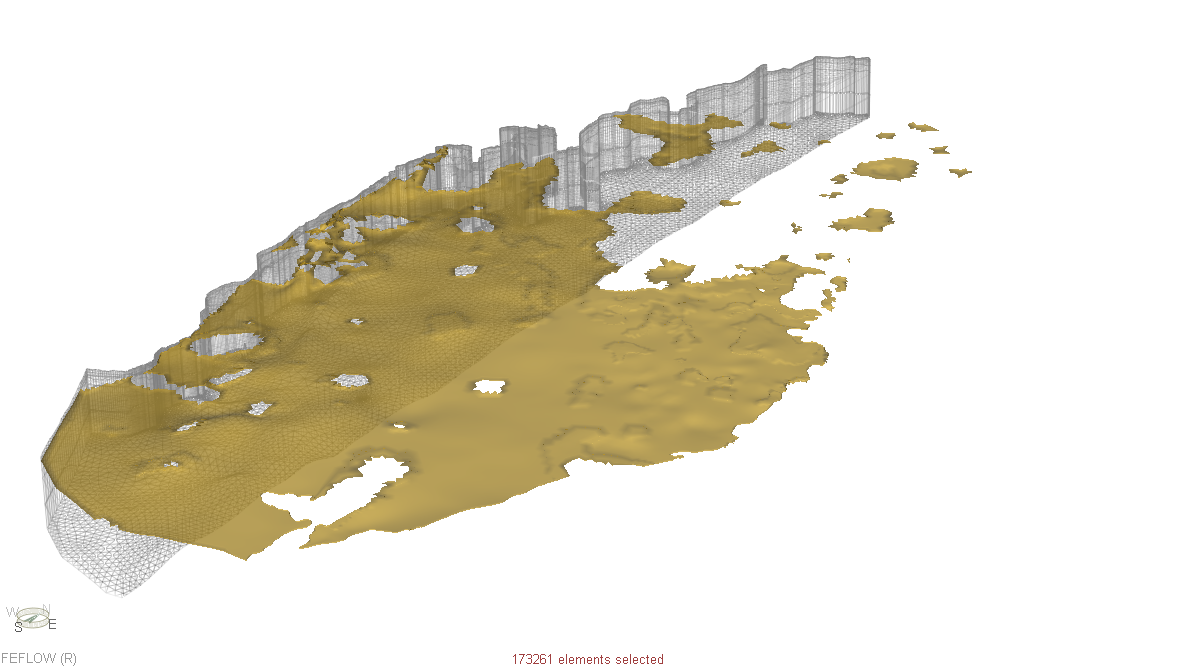
The Qatar Hydrogeological Assessment Project (QHAP) was launched to better understand Qatar’s groundwater systems and their link to geohazards such as karst processes and rising groundwater levels.
CLIENT
Ministry of Municipality State of Qatar (2023-2025)
WHAT WE DID
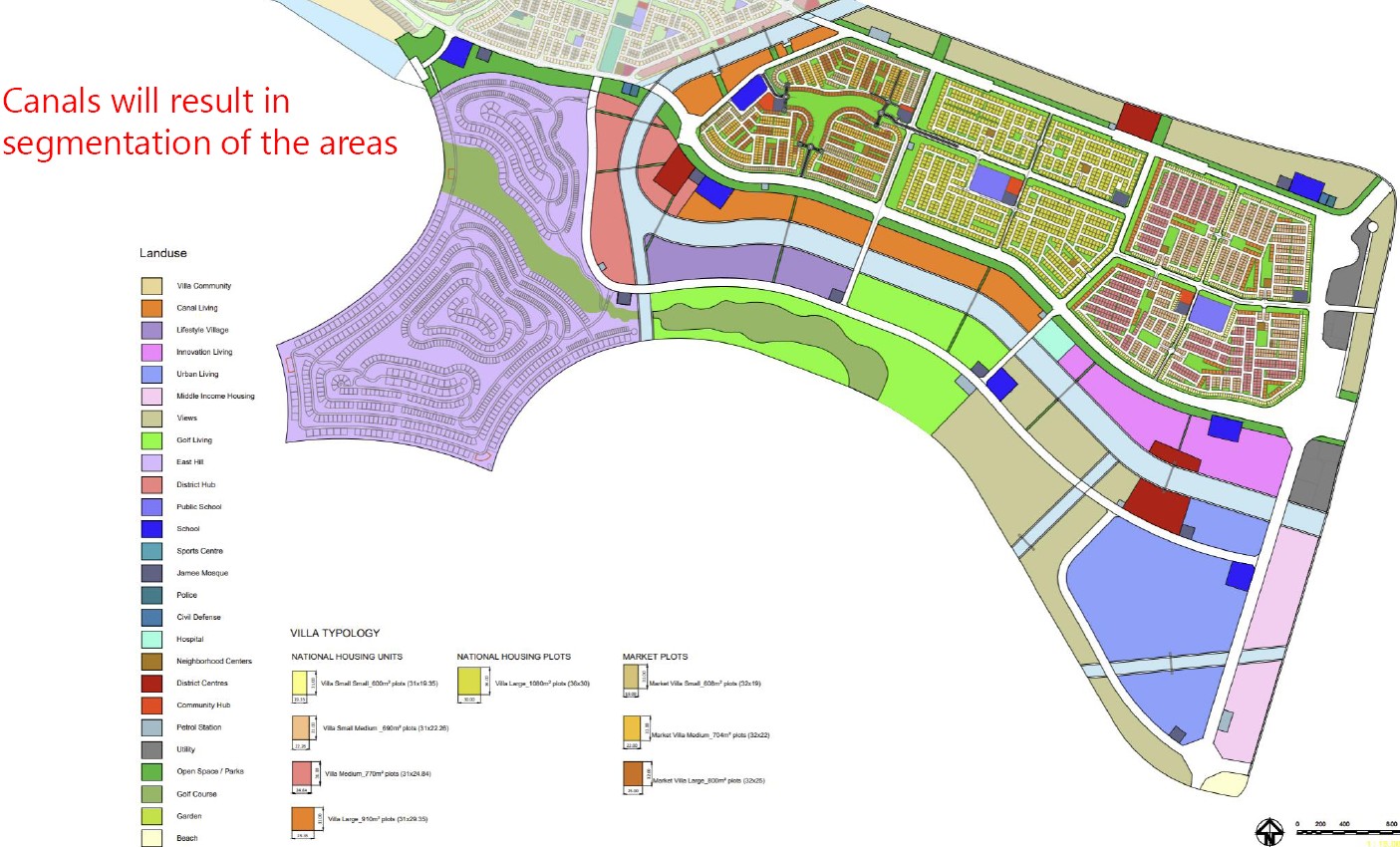
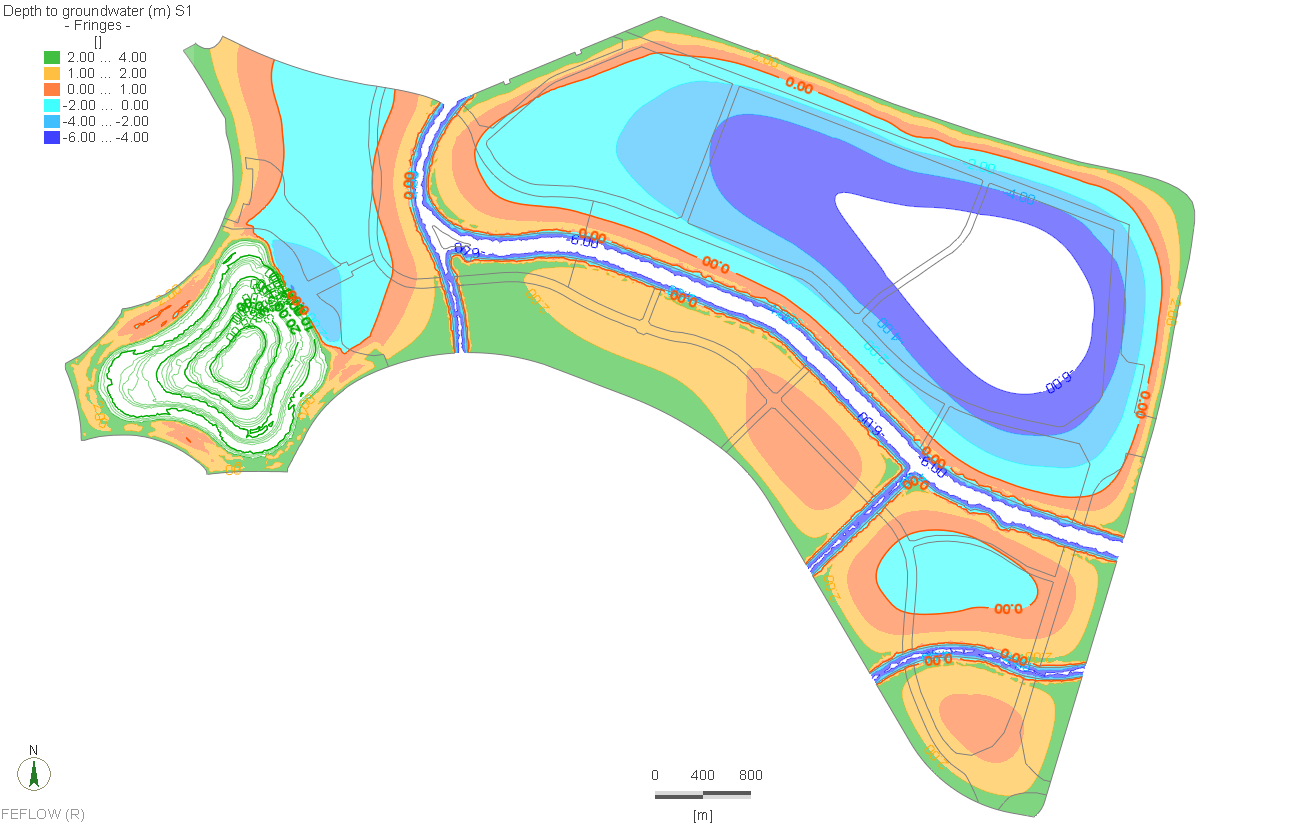
Rapid urbanization, agricultural abstraction, and major infrastructure works have significantly altered the natural hydrogeological balance, making a comprehensive national-scale groundwater model essential for planning and risk management.